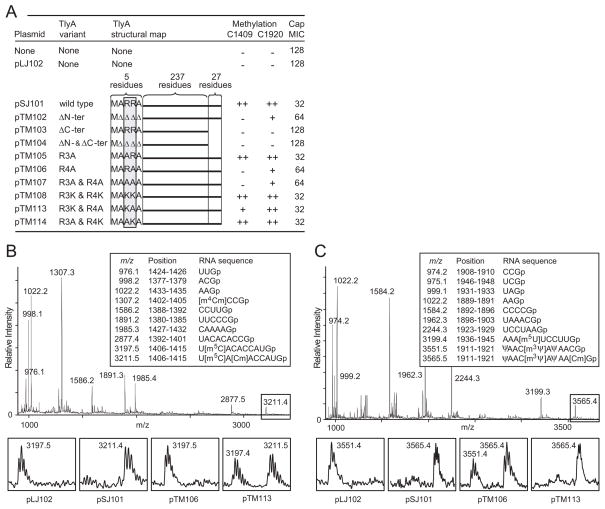
Fig. 4.
Methylation of rRNA by TlyA mutant enzymes in vivo.
A. Mutationsinthe N- and C-terminals of M. smegmatis TlyAII that affect the enzyme’s ability to methylate E. coli 16S and 23S rRNAs in vivo at nucleotides C1409 and C1920 (++, full; + partial; −, no methylation). Methylation levels were measured by both MALDI-MS and primer extension. Altered susceptibility of E. coli to capreomycin (Cap) is shown as MICs (μg ml−1); measurements in triplicate with identical results.Δ, deleted amino acid residue.
B. MALDI-MS analyses of 16S rRNA nucleotides 1377–1435 after RNase T1 digestion; rRNA from cells expressing wild-type TlyAII from pSJ101; boxes show the enlarged spectral region with nucleotide C1409 expressed from cells with different TlyA variants.
C. Corresponding MALDI-TOF MS analyses of 23S rRNA nucleotides 1889–1948 showing the enlarged peaks containing C1920. The measured m/z values (above the peaks) match the theoretical values (boxed) to within 0.1 Dalton.