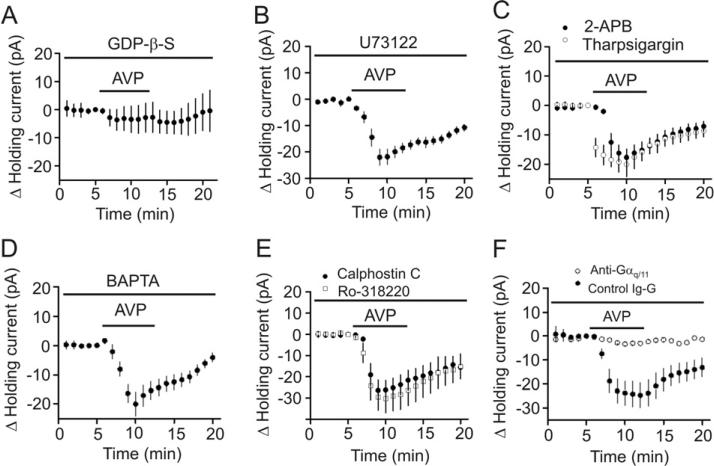
Fig. 5.
AVP-induced depolarization of hippocampal interneurons is dependent on Gαq/11 but independent of PLC, intracellular Ca2+ release and PKC. A, Inclusion of GDP-β-S (2 mM) in the recording pipettes blocked the effects of AVP on HCs. B, Pretreatment of slices with and continuous bath application of U73122 (10 μM) did not change AVP-induced increases in inward HCs. C, Pretreatment of slices with and continuous bath perfusion of 2-APB (100 μM) or intracellular application of tharpsigargin (10 μM) via the recording pipettes had no significant effects on AVP-induced increases in inward HCs. D, Intracellular perfusion of BAPTA (10 mM) via the recording pipettes had no significant effects on AVP-mediated increases in inward HCs. E, Pretreatment of slices with and continuous bath perfusion of calphostin C (1 μM) and Ro-318220 (1 μM) did not change AVP-induced increases in inward HCs significantly. F, Intracellular dialysis of anti-Gαq/11 antibody via the recording pipettes significantly reduced AVP-mediated increases in inward HCs but intracellular application of the control Ig-G did not alter AVP-induced increases in inward HCs.