Fig. 4.
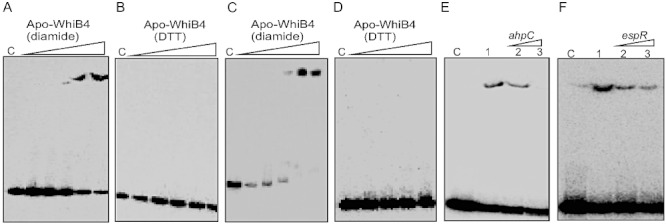
DNA binding activity of WhiB4. A–D. Apo-WhiB4 was prepared as described in Experimental procedures. The concentrations of apo-WhiB4 used for EMSAs were 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8 and 1 µM. EMSA reactions were performed with 0.2 nM γ-32P-labelled ahpC (A and B) and whiB4 (C and D) promoter DNA fragments. DNA binding of apo-WhiB4 in the presence of thiol-oxidant, diamide (A and C) or thiol-reductant, DTT (B and D). C: DNA binding in the absence of WhiB4 in each panel. E and F. Sequence preference of WhiB4 for DNA binding. EMSAs were performed using γ-32P-labelled ahpC promoter DNA with 800 nM of apo-WhiB4 in the presence of 50 mM diamide. The DNA binding was competed using increasing concentrations of unlabelled ahpC (specific) or espR (non-specific) promoter DNA. Lane 1 in (E) and (F): WhiB4:ahpC promoter complex. WhiB4 DNA binding was competed using 10-fold (lane 2) and 50-fold (lane 3) molar excess of either unlabelled ahpC (E) or espR (F) promoter DNA. C: DNA binding in the absence of WhiB4 in each panel.
