Fig. 8.
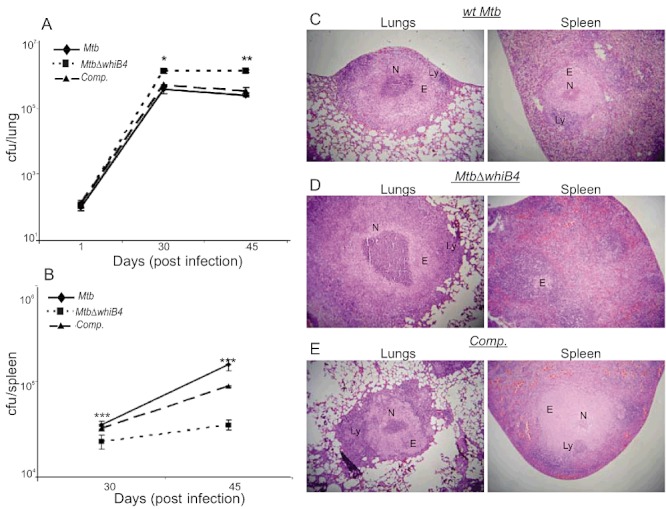
WhiB4 modulates in vivo survival and pathology of Mtb in guinea pigs. Outbred Hartley guinea pigs (n = 5) given an aerosol challenge of Mtb were assessed for bacterial burden in lungs (A) and spleen (B), and for the severity of lung and spleen pathology (C–E). Statistical significance for the pulmonic and splenic bacterial load was obtained by comparing wt Mtb and MtbΔwhiB4 strains: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Haematoxylin and eosin stained lung and spleen sections (30 days post infection) from guinea pigs infected with wt Mtb (C), MtbΔwhiB4 (D) and the whiB4 complemented (Comp.) strains (E). The pathology sections show granulomas containing areas of necrosis (N), epithelioid cells (E) and lymphocytes (L). All images were taken at 4× magnification. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.
