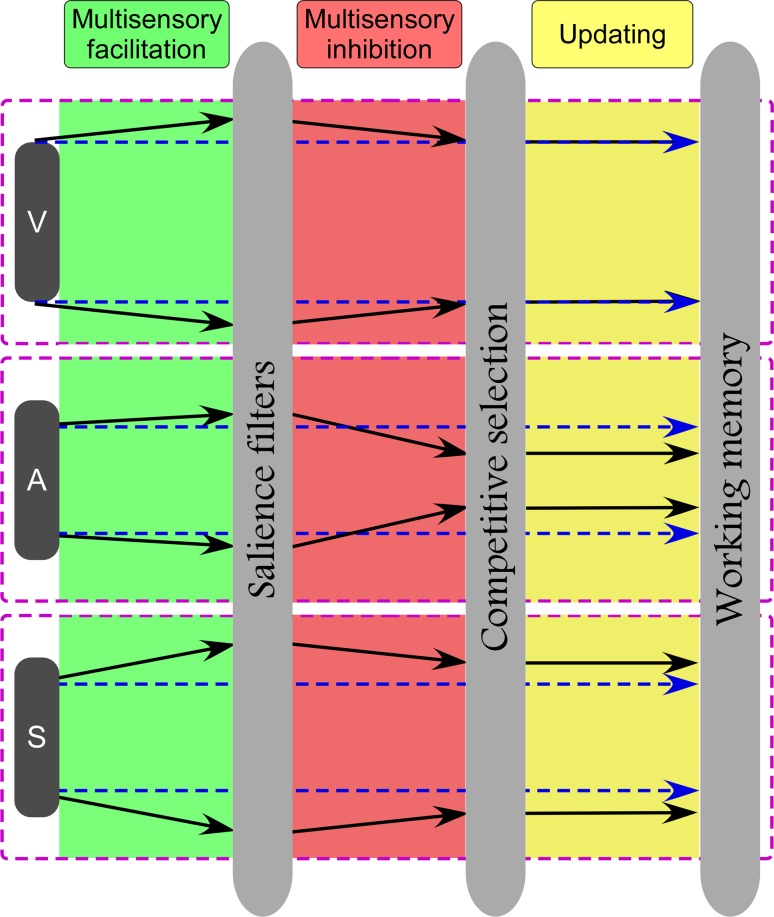
Fig. 7.
Dynamic model for modality-specific cognitive processing. Across all three modalities (vision, audition, and somatosensory), this modal would be comprised of three main parts: (1) Automatical salience filters; (2) Competitive selection; (3) Working memory updating. Blue dashed lines and black solid lines represent modality specific information flow without and with the influence of multisensory background events. Note that an increasing distance between two lines (either dashed or solid) for each modality represents a facilitation effect, and a decreasing distance between two lines for each modality represents a inhibition effect. Top panel: Similar multisensory facilitation and inhibition cancel out with each other, thus contributing to a balanced effect for visual target. Middle panel: The coexistence of appropriate multisensory facilitation and stronger inhibition, which occurred at early automatically salience filters and late competitive selection of neural representation, contributed to an overall multisensory inhibition for auditory target. Bottom panel: The coexistence of stronger multisensory facilitation and appropriate inhibition contributed to an overall multisensory facilitation for somatosensory target