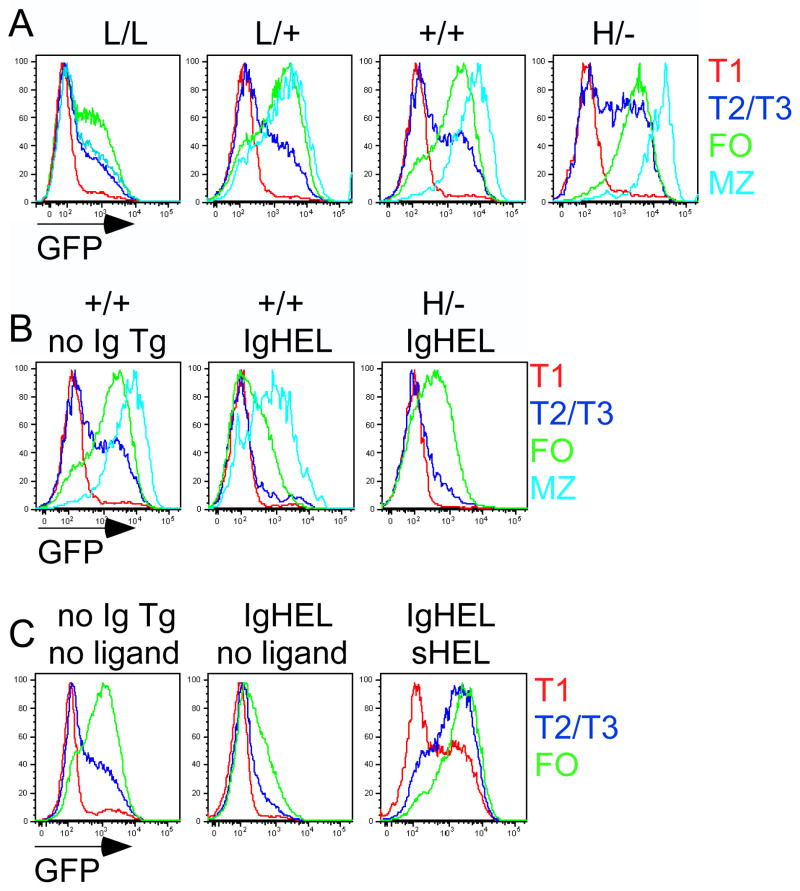
Figure 3. Expression of Nur77-GFP Bac Tg reporter is sensitive to genetic modulation of BCR signal strength and antigen.
(A) CD45 allelic series (low to high CD45 expression: L/L, L/+, +/+, H/−) GFPHI Tg splenic B cells were stained to identify B cell subsets as in Figure 2B, C. Overlaid histograms represent GFP expression in splenic subsets as gated in S5A.
(B) CD45+/+ GFPHI Tg and H/- (high CD45) GFPHI Tg splenic B cells with unrestricted (IgHEL-) or restricted (IgHEL+) repertoire in the absence of sHEL antigen were analyzed as in 3A. Overlaid histograms represent GFP expression in splenic subsets as gated in S5C.
(C) CD45+/+ GFPHI Tg splenic B cells with unrestricted (IgHEL-) or restricted (IgHEL+) repertoire in the presence or absence of sHEL antigen were analyzed as in 3A. Overlaid histograms represent GFP expression in splenic subsets as gated in S5D. All animals in Figure 3 were generated through genetic crosses. All data are representative of at least five independent experiments.