Figure 1.
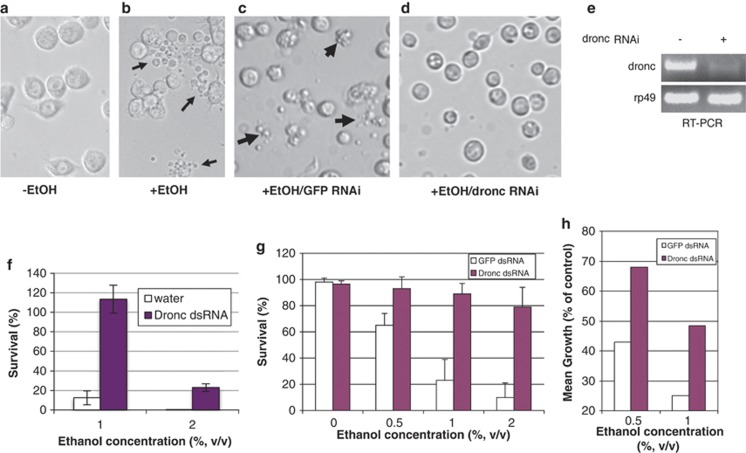
Dronc is required for alcohol-induced cell death. Micrographs of S2 cells untreated (a) and ethanol-treated (b) illustrates that alcohol challenge provokes extensive apoptosis, shown here 48 h postexposure to 2% ethanol (arrows in b and c indicate characteristic apoptotic cells and corpses). When cells are pretreated with irrelevant dsRNA (against GFP), ethanol challenge provokes widespread apoptosis (c). However, if parallel cultures are similarly pretreated with Dronc dsRNA, apoptosis is prevented (d). These data are corroborated and quantified in panels (f) and (g), where two different cell viability measures are used. (f) Control and Dronc dsRNA-treated cells were treated with indicated ethanol concentrations for 24 h and cell viability is measured using the Sytox assay (Sytox Green, Molecular Probes/Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). (f and g) Cell viability is measured using the CellTiter-Glo assay (see Materials and Methods). In both panels, cell survival (%) was normalized to control cells not treated with ethanol (mean±S.D., n=3). Dronc RNAi consistently reversed ethanol-induced killing, assayed here under two different treatment protocols. In these experiments, 20 000 cells were plated in wells that contained 0.5 μg of Dronc or GFP dsRNA, incubated for 2 (f) or 3 days (g) before 48 h of ethanol treatment. Under both protocols, silencing Dronc effectively prevents cell death. (e) Semiquantitative RT-PCR is shown validating effective silencing of Dronc RNA. Detection of rp49 here shows specificity of silencing. (h) Retention of proliferative capacity in ‘rescued' cells. Here, S2 cells were incubated with Dronc or GFP dsRNA for 3 days before re-plating at equal density followed by a 24-h challenge as indicated (in the presence of dsRNAs). Cells were then recovered and cultured in fresh media without ethanol for an additional 3 days. Relative growth in this post-treatment phase was determined by comparing ethanol challenged samples with untreated controls (average of two trials). Together, these studies establish that silencing expression of Dronc prevents apoptosis and preserves cell viability in the context of alcohol challenge