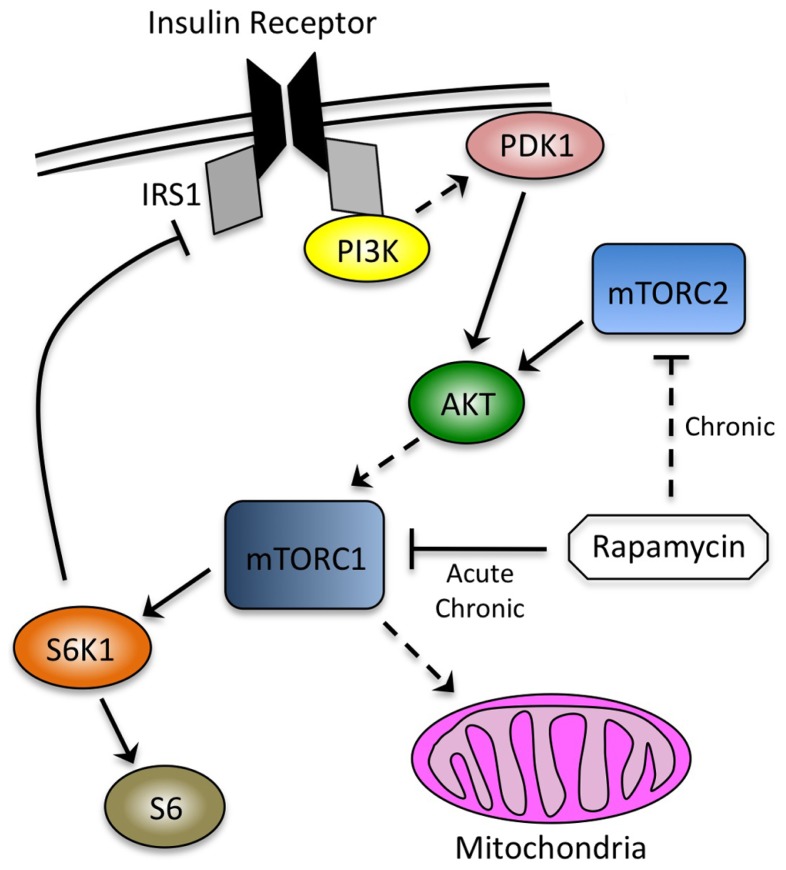
FIGURE 1.
Interdependence of signaling through the insulin receptor and mTOR. mTORC1, the canonical target of rapamycin, is downstream of the insulin signaling cascade and mediates negative feedback through S6K1. mTORC2 is an AKT kinase that is not sensitive to acute rapamycin treatment (~ h), but can be inhibited by chronic exposure (~24 h). Phosphorylation of AKT by PDK1 and mTORC2 occurs at discrete sites (threonine 308 and serine 473, respectively). mTORC1 promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, although the relevance of this observation to its effects on insulin sensitivity has not been established. Solid lines indicate direct effects, whereas dashed lines indicate intermediate steps, or in the case of rapamycin inhibiting mTORC2, the requirement for chronic exposure.