Figure 10.
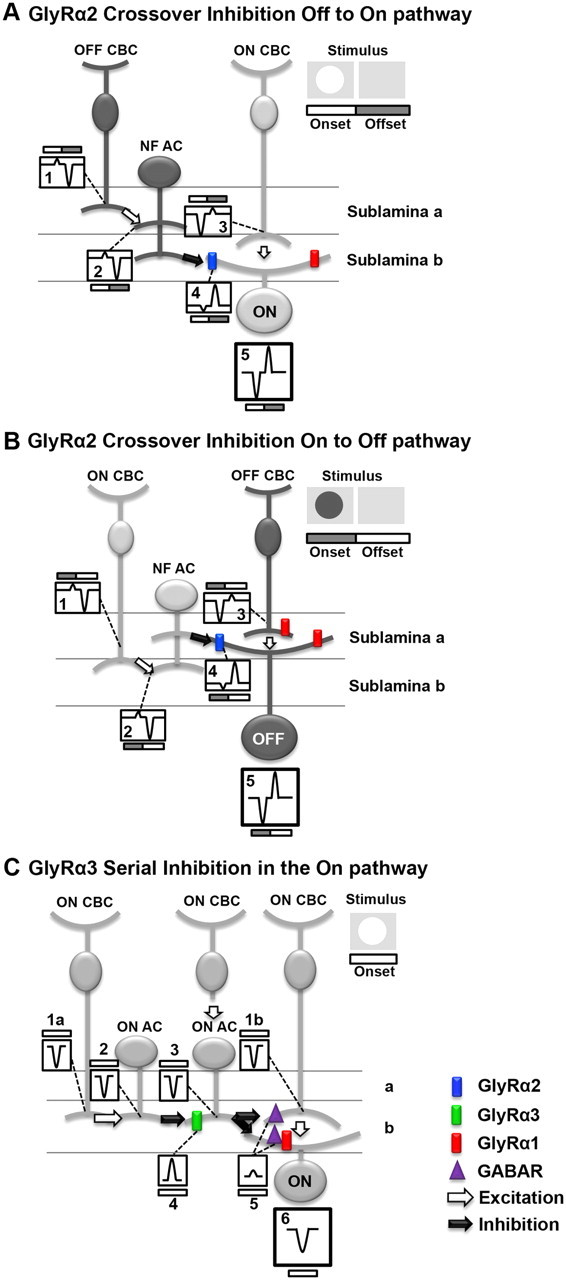
GlyRα2 and GlyRα3 mediate inhibition using different inhibitory circuits. A–C, Schematic diagrams of the proposed roles of GlyRα2 and GlyRα3 in the WT mouse On and Off retinal pathways are shown. Each diagram illustrates a basic retina circuit that is consistent with the results presented. The diagrams in the top right corners illustrate the stimulus and the timing of its onset and offset. Within each circuit, the numbered boxes represent the current evoked at stimulus onset and offset. Nota bene: Currents are represented with transient time course for simplicity. The currents in the boxes do not reflect the temporal properties of the currents, as described in Results. A, GlyRα2 mediates crossover inhibition from the Off to the On pathway. At stimulus onset (white bar), the NF AC is driven by an OFF CBC (Box 1), which produces a small outward current (Box 2). The NF AC, using a crossover inhibitory mechanism, inverts the polarity of the current via GlyRα2 (blue), producing a current in the ON GC (Box 4) that enhances the current from its presynaptic ON CBC (Box 3). At stimulus offset (gray bar), a similar mechanism transfers an inverted polarity current from the Off to the On pathway, which enhances poststimulus suppression. The spiking response of the GC is governed by the summation of the inputs (Box 5). B, GlyRα2 mediates crossover inhibition from the On to the Off pathway. Similar to the description in A, at stimulus onset (gray bar), the NF AC is driven by an ON CBC (Box 1), which produces a small outward current (Box 2). The NF AC, using a crossover inhibitory mechanism inverts the polarity of the current via GlyRα2 (blue), producing a current in the OFF GC (Box 4) that enhances the current from its presynaptic OFF CBC (Box 3). At stimulus offset (white bar), a similar mechanism transfers an inverted polarity current from the Off to the On pathway, which enhances poststimulus suppression. The spiking response of the GC is governed by the summation of the inputs (Box 5). C, GlyRα3 mediates serial inhibition in the On pathway. At stimulus onset (white bar), ON CBCs depolarize (Boxes 1a and 1b represent currents in all CBCs). The ON CBC (far left) targets an ON AC producing an inward current (Box 2). Using GlyRα3 (green), this distal ON AC produces an outward current in the proximal ON AC (Box 4), which is summed with the inward current produced via input from its presynaptic ON CBC (Box 3). The proximal ON AC targets either the ON CBC (far right) at a GABA receptor (purple) or an ON GC at either a GABA receptor (purple) or a GlyRα1R (red). Because the proximal ON AC output is controlled by its ON AC inhibitory input, the outward current (Box 5) is small. Depending on the postsynaptic target of the proximal ON AC, the GCs total current (Box 6) reflects either the input from its presynaptic CBC (Box 1b) or from the inputs from its presynaptic CBC and ON AC (Box 5).
