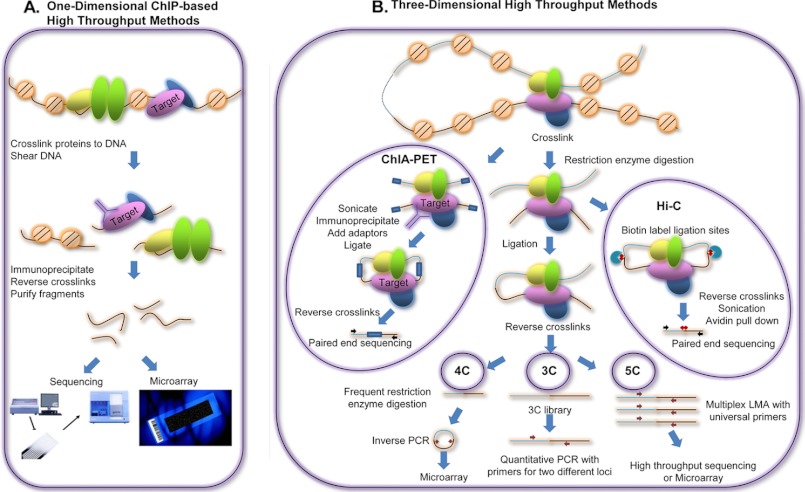
FIGURE 1.
Experimental techniques to investigate TFBSs and chromatin interactions. A, schematic representation of major steps in one-dimensional ChIP-based high throughput methods used to identify TFBSs. Briefly, cells are treated with formaldehyde to cross-link the TFs to genomic binding sites, the genomic DNA is sheared, and bound fragments are selected by immunoprecipitation using an antibody to a TF of interest. The cross-links are then reversed, and the fragments are purified and applied to microarrays (ChIP-chip) or sequenced (ChIP-seq). B, assays used to study three-dimensional chromatin structure. ChIA-PET is similar to ChIP in that fragments bound to a TF of interest are immunoprecipitated. However, unlike ChIP assays, fragments brought into close proximity by DNA looping are ligated prior to the immunoprecipitation step. Hi-C is similar to ChIA-PET in that fragments in close proximity are ligated. However, Hi-C does not rely on immunoprecipitation by an antibody to a TF but rather uses biotin labeling of the ligation sites, followed by avidin-based purification. The fragments are then subjected to paired-end sequencing. The 3C, 4C, and 5C assays also detect pairs of genomic loci that are in close proximity in the three-dimensional space of the nucleus. Formaldehyde is used to cross-link spatially close chromatin regions, the DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme, and fragments within the cross-linked complexes are joined by ligation. In 3C, the joined regions are analyzed using PCR. In 4C, a second enzyme restriction digestion step is performed to shorten the hybrid fragments, which are circularized and subjected to inverse PCR; the products of inverse PCR are hybridized to a custom microarray. In 5C, a LMA step allows the ligation junctions of all the hybrid fragments in the 3C library to be analyzed using microarrays or next-generation sequencing. Note that this figure shows greatly simplified versions of the different technologies; for detailed descriptions, please see the original papers.