FIGURE 2.
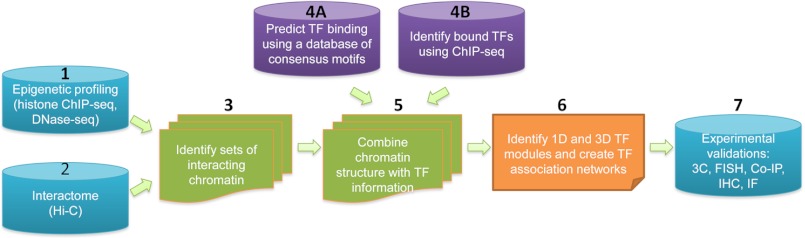
Pathway to identify one- and three-dimensional TF modules. The steps in identifying TF modules include the following: step 1, perform epigenomic profiling (histone ChIP-seq) and identify open chromatin (DNase-seq) in the cell type of interest; step 2, identify interacting chromosomal loci in the same cell type using the Hi-C method; step 3, use the epigenomic data to cluster the interacting chromosomal loci into distinct sets; step 4, either predict TF binding using a data base of TF consensus motifs (4A) or identify bound TFs using experimental ChIP-seq data (4B); step 5, integrate the chromatin structure information with the TF binding information; step 6, create one-dimensional (1D) and three-dimensional (3D) TF modules and TF association networks using computational methods such as the Apriori algorithm, a Bayesian approach, or a neural network; step 7, experimentally validate TF associations via methods such as 3C, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH), co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF).
