FIGURE 4.
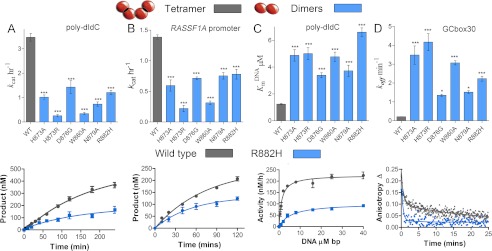
DNMT3A homodimers and homotetramers are active with different mechanisms. Disruption of the dimer interface reduces activity, but the dimers are still active with increased off-rates. The wild type tetramers are labeled gray and the dimer mutants are labeled blue. A and B, kcat values of DNMT3A wild type and oligomeric mutants were determined on multisite substrates, poly-dIdC (A), and the human promoter RASSF1A (B.). Below are the wild type (gray) and dimer mutant R882H (blue) time course trace. C, eliminating tetramer formation in DNMT3A increased KmDNA (substrate poly-dIdC), above is the bar chart of KmDNA values, and below are the kinetic fits. D, DNMT3A homodimers have an increase in off-rate compared with homotetramers, above is the bar chart of koff values determined on GCbox30, and below are the kinetic fits. All error bars were determined from at least three experiments given as S.E.; one-way analysis of variance was used to compare wild values to each mutant. *, p > 0.05; **, p > 0.01; ***, p > 0.001.
