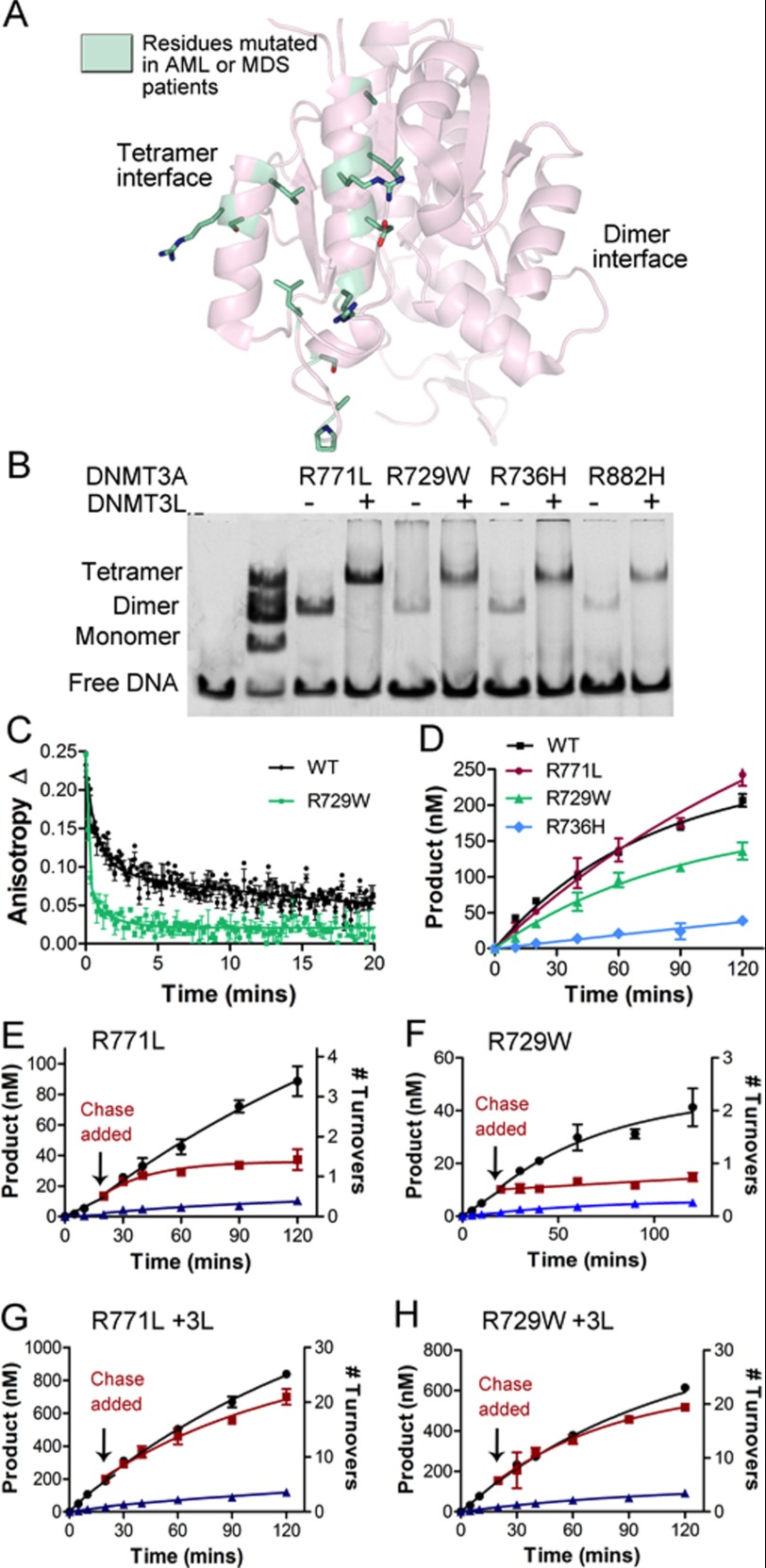
FIGURE 7.
AML mutants disrupt the tetramer interface and eliminate DNMT3A processivity. A, mutants identified in AML and MDS patients located along DNMT3A tetramer interface. B, AML mutants at the tetramer interface disrupt the homotetramer and form heterotetramer with DNMT3L. C, the rate of catalysis is minimally changed for two of the tetramer interface disrupting mutants (R771L and R729W). D, disruption of the tetramer interface increases the off-rate. E and F, disruption of the tetramer interface also eliminates processivity, as demonstrated by the processive chase assay (E, R771A; F, R729W). G and H, DNMT3L restores processivity by forming a heterotetramer (G, R771A; H, R729W). The chase assay was done as follows: ●, only substrate (20 μm bp RASSF1A); ■, substrate and then 400 μm bp chase (pCpGL) at 20 min; ▴, substrate and pCpGL at the start of the reaction.