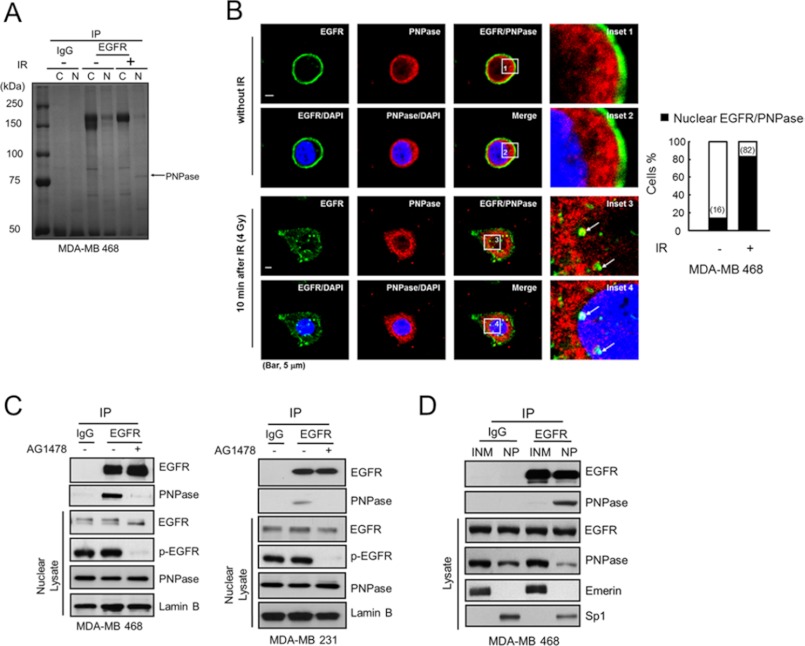
FIGURE 1.
Nuclear EGFR interacts with PNPase. A, MDA-MB 468 cells were treated with or without 4 Gy ionizing radiation (IR). After 10 min, the cytosolic or nuclear lysate was extracted and immunoprecipitated with IgG or anti-EGFR antibody and separated by SDS-PAGE. The major band near 75k Da as indicated was identified as PNPase by tandem mass (MS/MS) spectrometry. B, left, co-localization of EGFR (green) and PNPase (red) in the nucleus (blue) at 10 min post-IR was examined by immunofluorescence staining and observed under a confocal microscopy. The arrows in insets 3 and 4 indicate the colocalized EGFR and PNPase in the nucleus, which is shown in yellow in the merged image. Scale bar, 5 μm. Right, bar graph shows the percentage of the 50 counted cells with colocalized EGFR and PNPase. C, interaction between EGFR and PNPase in nuclear lysate from MDA-MB 468 and MDA-MB 231 cells were verified by IP (immunoprecipitation)/IB (immunoblotting) with anti-EGFR/anti-PNPase antibody, respectively. Cells were treated with or without 10 μm AG1478 for 12 h, and the interaction of EGFR and PNPase in the nucleus was examined. D, purified inner nuclear membrane (INM) and nucleoplasm (NP) portions were immunoprecipitated using the indicated antibodies followed by IB in MDA-MB 468 cells. Eemerin, and Sp1 were used as markers for the INM, and NP, respectively. IP performed with IgG was used as a negative control.