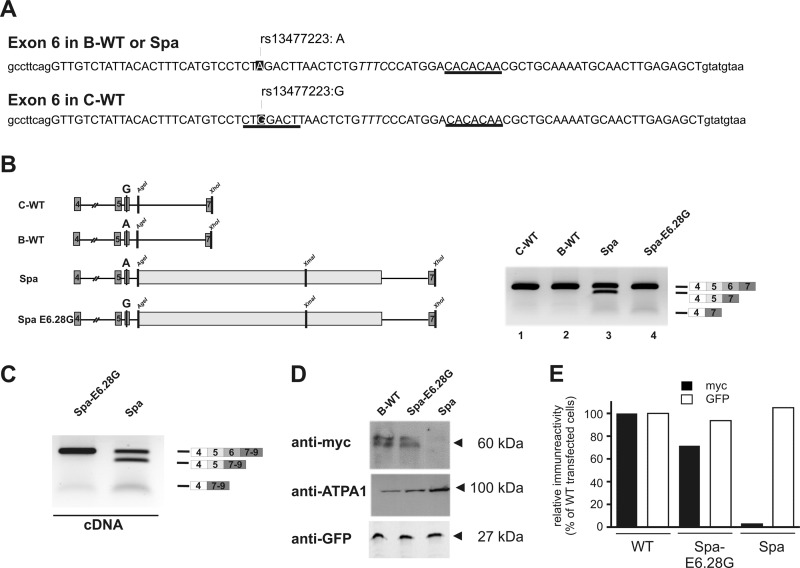
FIGURE 3.
LINE1-associated skipping of exon 6 depended on a polymorphic residue at position E6.28. A, sequence of the Glrb exon 6 from C57BL/6J and C3H/HeJ mice, including the surrounding intronic regions. Exonic sequence is displayed in uppercase letters. Sequence motifs predicted to bind to SRSF1 are indicated. Note that one SRSF1 site predicted E6.23 in the C3H/HeJ exon 6 was not detected in the C57BL/6J due to a SNP at position E6.28 (A, strain C57BL/6J; G, strain C3H/HeJ; dbSNP, rs13477223). B, the effect of the SNP at position E6.28 was analyzed by introducing a G at E6.28 in the Spa minigene. The indicated minigenes were transfected into HEK293 cells and exon skipping was analyzed by RT-PCR. Note that mutation of E6.28 in the Spa minigene to a G (Spa-E6.28G) was sufficient to prevent skipping of exon 6. C, B-WT, Spa, and Spa E6.28G minigenes were complemented to full-length ORFs by adding coding sequences of the Glrb exons 1–3, including an N-terminal Myc tag and at the 5′ end and coding sequences of the exons 8–9 at the 3′ end of the minigene. The constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells and exon skipping was analyzed by RT-PCR using primers positioned in exons 4 and 9. D, membrane preparations form HEK293 cells transfected with the minigenes containing the full-length GlyR β ORF as indicated and for testing transfection efficiencies a plasmid encoding for GFP, were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. The blots were probed with antibodies against Myc, ATPA1, and GFP. E, expression levels from the experiment shown in D as quantified by scanning of the blots and densitometric analysis using NIH ImageJ software. Note that in contrast to samples from WT and Spa-E6.28G transfected cells, samples from Spa transfected cells, showed almost no Myc immunoreactivity although the cells were transfected efficiently as indicated by GFP immunoreactivity.