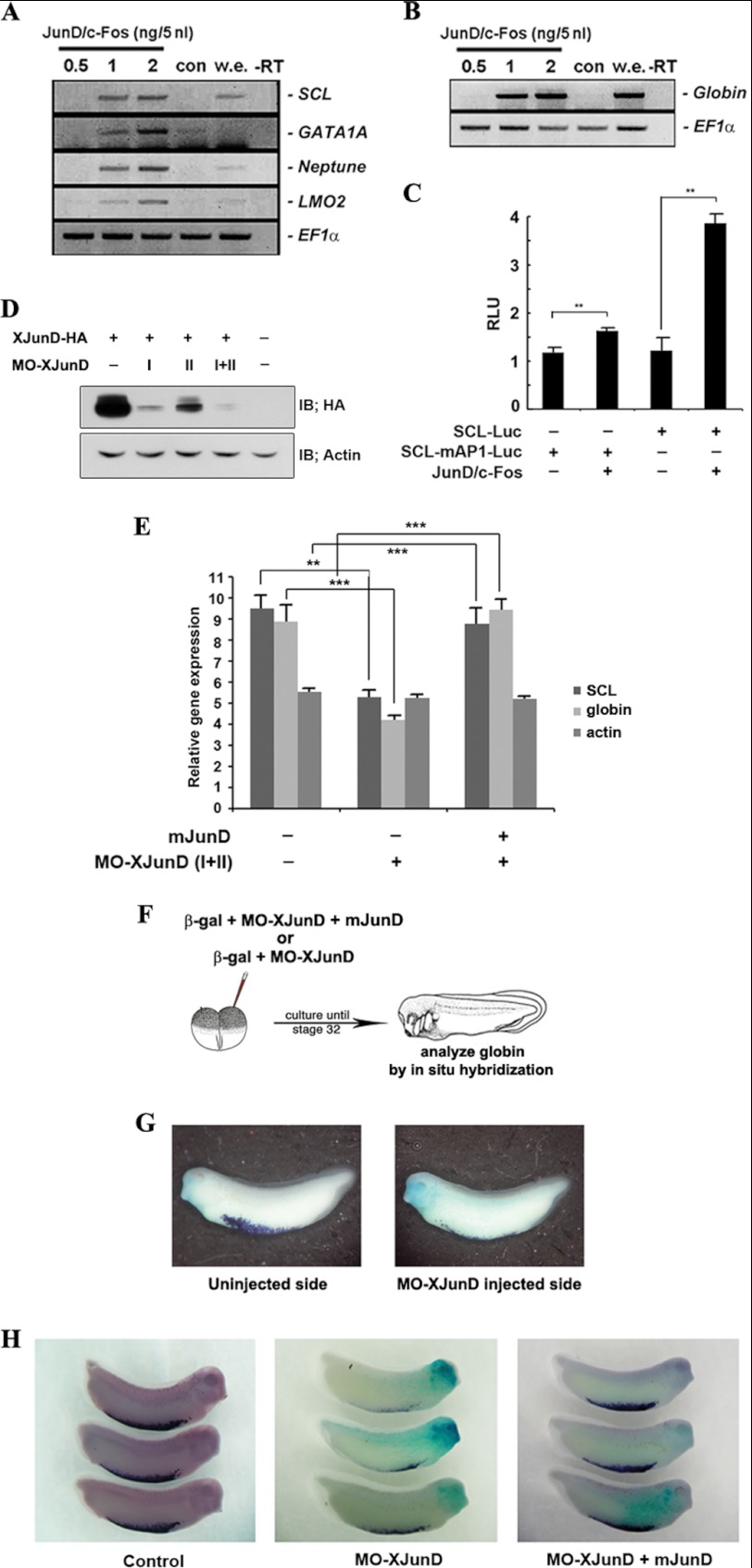
FIGURE 1.
AP-1JunD/c-Fos is required for hematopoiesis. A and B, co-expression of junD and c-fos induces hematopoietic makers (SCL, GATA1A, Neptune, and LMO2) and globin. Animal caps, explanted from embryos injected with the indicated concentration of mRNAs encoding junD or/and c-fos, were incubated until stages 18–20 (A) or 24–28 (B) and used for qRT-PCR analysis. C, co-expression of junD and c-fos enhances the promoter activities of the SCL but not the mutant SCL-mAP1. Embryos injected with the SCL- or SCL-mAP1-luciferase reporter gene alone or together with 2 ng of junD and c-fos were incubated until stages 18–20. Luciferase activity was measured. Values are shown as means ± S.D. from at least three independent experiments. RLU, relative luciferase activity. D, MO junD (20 ng) specifically knocks down the translation of the overexpressed C-terminal HA-tagged XJunD protein at stage 18. Actin served as a specificity control. E, mouse junD rescues SCL and globin, which are repressed by MO junD expression without changing the dorsal mesoderm marker, actin. qRT-PCR analysis of whole embryos expressing MO junD (20 ng) alone or in combination with 1 ng of mouse junD at stages 20–24. F, illustration of the scheme of the experiment. One blastomere of two-cell embryos was injected with mRNA encoding β-galactosidase together with MO junD (20 ng) or mouse junD (1 ng) (mjunD) as illustrated. G and H, embryos were stained for β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity at stage 30 (blue stain) followed by in situ hybridization analysis of globin expression (purple stain). G, the expression of globin is repressed in the MO junD-injected side. H, mouse junD mRNA (mjunD) rescues globin expression that is repressed by expression of MO junD. EF1α, loading control; w.e., whole embryo was used as a positive control for PCR; −RT, control reaction without reverse transcriptase; con, animal cap samples obtained from non-injected embryos. **, p value < 0.01; ***, p value < 0.001. IB, immunoblot.