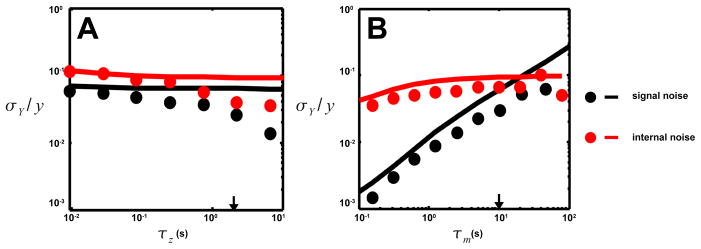
Fig. 3.
The dependence of the total internal noise floor (red) and the total signal noise (black) on A. the output decay time τz and B. the adaptation time τm. The total signal noise is the sum of the three signal noises from Figure 2. The total internal noise has contributions from both receptor adaptation and signal degradation. The total signal noise, dominated by the random-walk induced noise, is comparable to the internal noise. At low τm ~ τz adaptation noise starts being reduced by time averaging and the internal noise drops. Deviations between simulations (symbols) and linear analysis (lines) come from strong nonlinear effects when τz/τy ≫ 1.