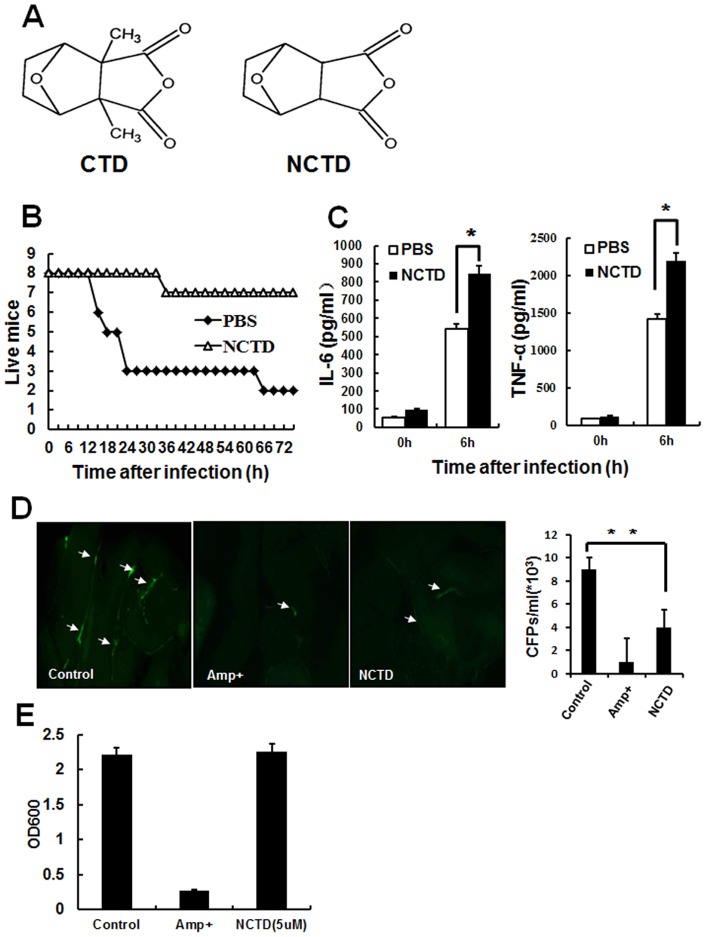
Figure 1. NCTD protects mice from bacterial-induced peritonitis.
A, Chemical structure of NCTD and CTD. B, The survival of peritonitis mouse was increased by NCTD obviously. The mice were treated with NCTD or PBS at 24 h and 6 h before infection. Both NCTD and PBS (containing 0.1% DMSO) treated mice (n = 8) were intraperitoneal injected with E.coli 0111 (8*107) and monitored every 3 h for 72 h. C, Serum concentration of IL-6 and TNF-α in mouse model was enhanced by NCTD. The blood was obtained 6 h after infection and the serum concentration of IL-6 and TNF-α was measured by ELISA assay. (*, P<0.05) Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. D, The quantity of bacterial was reduced in NCTD treated mouse. The mice were treated with 1 ml vehicle control (containing 0.1% DMSO), 100 ug/ml Ampicillin or NCTD (10 mg/kg) respectively followed by an i.p injection with 5×107 CFU of E. coil-GFP in 1 ml PBS for 16 h. Then the bacteria resident in abdomen was visualized by fluorescent stereomicroscope. Also, their peritoneal cavities were lavaged with 3 ml PBS, and bacterial counts were determined by plating on agar plates. n = 4 mice per group. E, NCTD has no effects on the growth of E. coil-GFP. E.coli-GFP were cultured with 100 µg/ml Ampicillin (Amp+) and 5 μM NCTD for 24 h respectively. Then the bacteria number was detected by spectrophotometer. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results (mean ± s.d. in B, D).