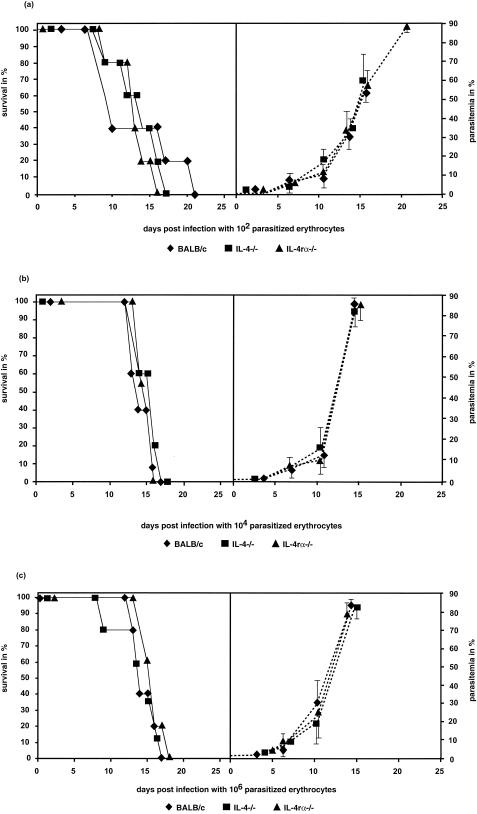
FIG. 2.
Survival (solid lines) and parasitemia (dotted lines) of BALB/c, IL-4−/−, and IL-4rα−/− mice infected with 102 (a), 104 (b), or 106 (c) parasitized erythrocytes of the P. berghei ANKA strain. All groups showed a 100% mortality rate. Increases in the infection dose led to higher parasitemia (b and c) but not to significantly earlier death due to cerebral malaria. Statistical analyses of the survival rates were done with the Kaplan-Meier test. No differences were found between the wild-type control versus the IL-4−/− and IL-4rα−/− mice. Each group contained five animals. The data are representative of two independent experiments. The parasitized erythrocytes were prepared from one highly infected BALB/c mouse. All groups of mice were infected with this batch to avoid differences in the survival rates in one experiment due to different viabilities of the parasites.