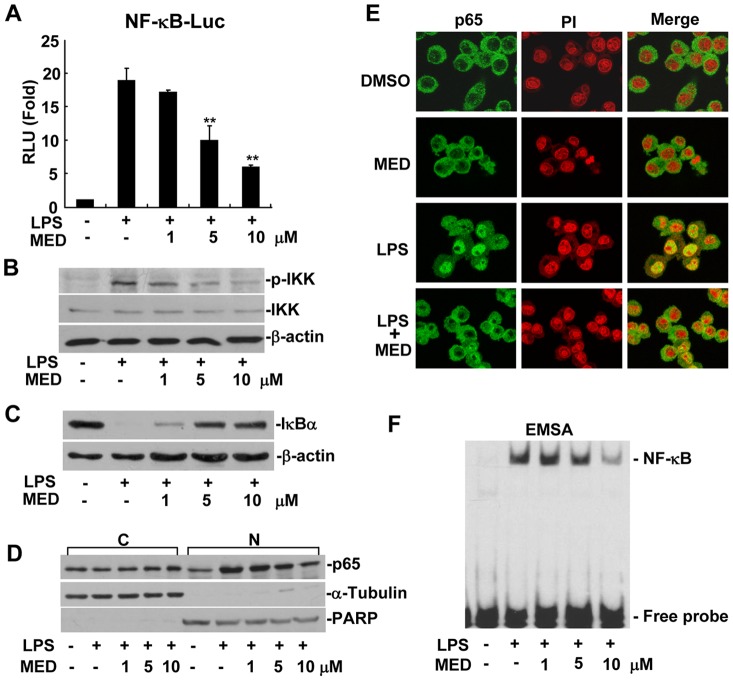
Figure 4. MED suppresses LPS-induced NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 cells.
A. Effect of MED on NF-κB luciferase reporter activity after LPS treatment. Cells were transiently transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids and incubated overnight, then cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) together with various doses of MED for 6 h. Luciferase activities were determined as described in the Methods. Data shown are the mean + SD (n = 3). **p<0.01. B. Effect of MED on phosphorylation of IKK induced by LPS. Cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) together with various doses of MED for 10 min. C. Effect of MED on degradation of IκBα induced by LPS. Cells were treated by LPS (100 ng/ml) together with various doses of MED for 15 min. D, E. Effect of MED on nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 induced by LPS. Cells were treated by LPS (100 ng/ml) together with various doses of MED for 30 min, then nuclear translocation of p65 was determined by Western blotting (D) or Immunofluoresence analysis (E). C: Cytoplasm; N: Nucleus. The area of nucleus was marked with PI. F. Effect of MED on DNA binding activity of NF-κB induced by LPS. Cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) together with various doses of MED for 30 min. Nuclear extracts were obtained for EMSA.