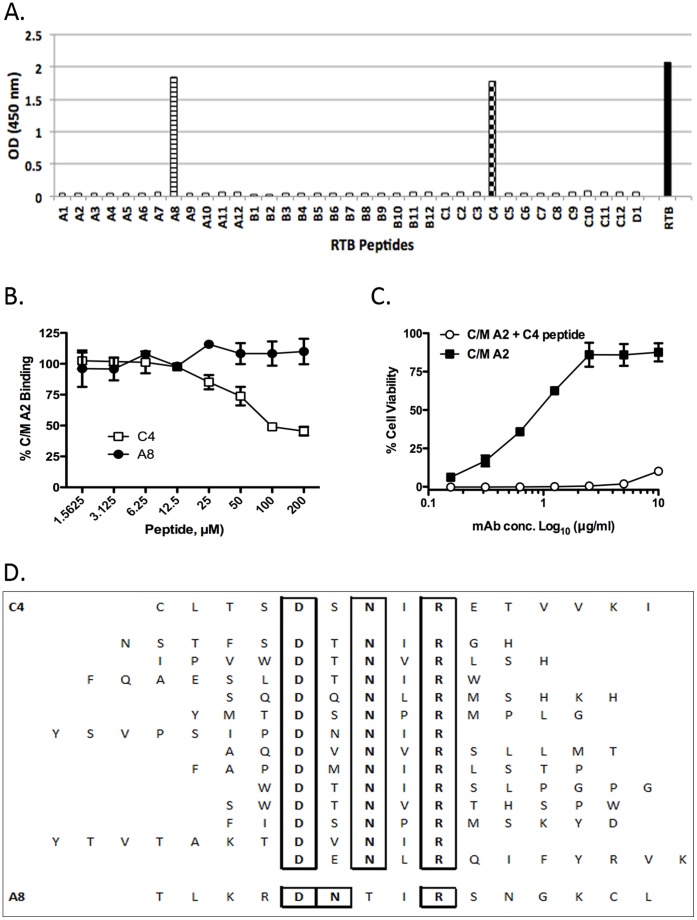
Figure 9. Delineation of the C/M A2 epitope using pepscan analysis and phage display.
(A) C/M A2 (10 μg/ml: 67 nM) was examined by ELISA for the ability to bind to an RTB peptide array consisting of 37 15-mers (A1-D1, x-axis), each overlapping its neighbors by 8 amino acids 32]. C/M A2 reacted with peptides C4 and A8, corresponding to residues T50-L64 (TLKRDNTIRSNGKCL) spanning sub-domains 1β and 1γ and residues C190-I204 (CLTSDSNIRETVVKI) in sub-domain 2β, respectively. Data is representative of 2 independent experiments. (B) A competition ELISA in which 96-well microtiter plate coated with RTB was probed with C/M A2 in the presence of increasing concentrations of peptides C4 and A8. (C) A competition cytotoxicity assay in which ricin (10 ng/ml) was incubated for 1 hr with C/M A2 mAb at the indicated concentrations in the presence or absence of soluble C4 peptide (10 mM) before being applied in triplicate to Vero cells grown in 96-well microtiter plates. Cell viability was assessed 48 hr later. Data is representative of 2 independent experiments. (D) A phage displayed 12-mer peptide library was subjected to affinity enrichment against immobilized C/M A2 mAb, as described in Materials and Methods. The 13 unique sequences identified following 3 rounds of C/M A2 selection are aligned vertically and compared to peptides C4 (top) and A8 (bottom). All 13 phage-derived sequences contained a DxNxR motif (as well as a hydrophobic residue in the 4th position) that aligned exactly with the C4 peptide.