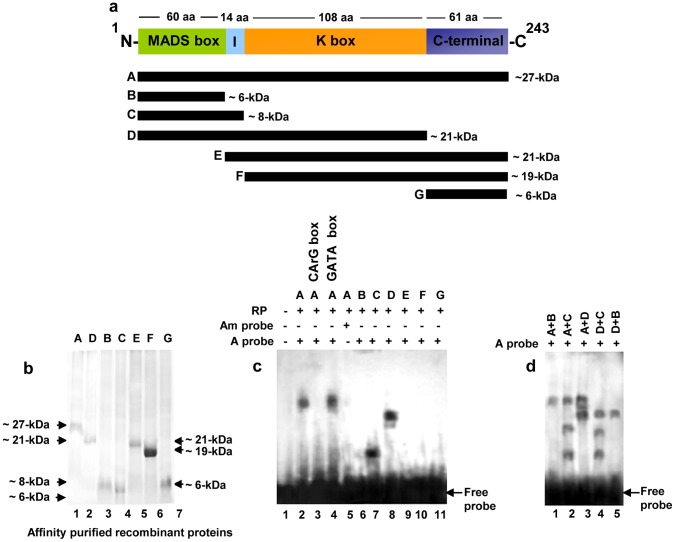
Figure 2. Homodimer formation by MA-MADS5. a.
Schematic representation of the domain structures of putative MA-MADS5 protein obtained using CDD, SMART and Proscan database analyses. Deleted versions of the wild type full-length protein have been shown. The molecular mass of each protein fragment has been indicated at the right side. b Coomassie blue stained gel showing affinity purified fraction of recombinant wild type and different deletion versions of MA-MADS5 proteins. Molecular mass markers are shown on the left and right. c Gel mobility shift assay with recombinant wild type and truncated forms of MA-MADS5 proteins using labeled CArG box motif as probe (A probe). No protein was added in lane 1, while lanes 2–4 contained 2 µg purified recombinant wild type protein (A) incubated with labeled CArG-box DNA probe. Lane 3 contained 100-fold excess of unlabeled CArG box motif as competitor. Lane 4 contained 100-fold excess of unlabeled GATA box motif as non-specific competitor. Lane 5 contained labeled modified CArG box motif as probe (Am probe) with wild type recombinant MA-MADS5. Lanes 6 to 11 correspond to gel shift assays using various deletion versions of recombinant MA-MADS5 (B, C, D, E, F and G) with labeled oligo containing the CArG box motif as probe. d Detection of dimerization of MA-MADS5 protein by gel mobility shift assay. Formation of heterodimers between wild type and various deletion versions of recombinant MA-MADS5 protein (MIKC with M, MI and MIK or A+B, A+C, A+D respectively) and among the deletion fragments of MA-MADS5 like proteins (MIK with MI and M or D+C, D+B) were detected as relative band shift. Representative images from at least three independent experiments are shown for Figure b–d. M, I, K and C represent the MADS-box, I-region, K box and C-terminal domains of MA-MADS5, respectively.