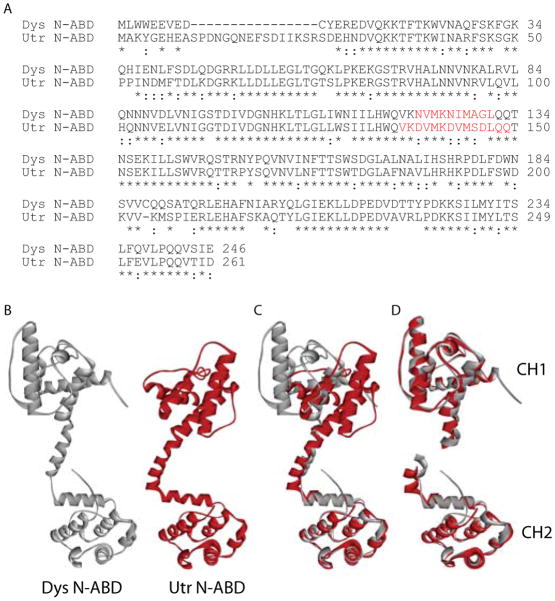
Fig. 1.
Sequence and structural comparison of the N-ABDs. A. Amino acid sequence alignment of the N-ABDs of human dystrophin (Dys; DMD gene product) and utrophin (Utr; UTRN gene product) using the ClustalW2 program 70 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/). Residues marked with an asterisk (‘*’) indicate identical residues and those marked with a colon (‘:’) indicate highly conserved residues. Figure also shows the α-helix connecting the two CH domains (red colored residues). B. X-ray crystal structures of dystrophin (Dys) and utrophin (Utr) N-ABDs 41,42. C. Structural alignment of the N-ABDs using the MultiProt program 71 (http://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/MultiProt/). D. Structural alignment of the corresponding CH1 (N-terminal) and CH2 (C-terminal) domains in the two N-ABDs using the MultiProt program. In panels B – D, gray and red colored structures represent dystrophin and utrophin N-ABDs respectively. Molecular structures were drawn using the program Accelrys Discovery Studio Visualizer (http://accelrys.com/products/discovery-studio/visualization-download.php).