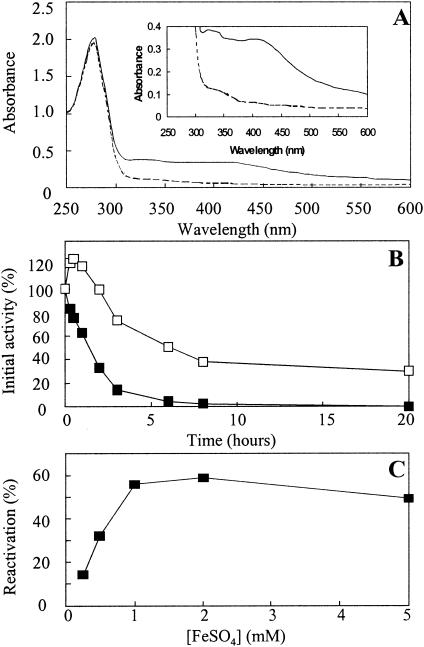
FIG. 5.
SdaA is an oxygen-labile iron-sulfur enzyme. (A) UV/visible spectra of active pure l-serine dehydratase (solid line) measured under anaerobic conditions and air-inactivated l-serine dehydratase (broken line), showing loss of absorbance at 420 nm (characteristic of iron-sulfur enzymes) upon exposure to air. (B) Inactivation kinetics of l-serine dehydratase in air. SdaA in 20 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, was incubated at 4°C under anaerobic conditions (□) or in the presence of air (▪). Samples were withdrawn at the indicated time points and were assayed under anaerobic conditions for l-serine dehydratase activity as described in Materials and Methods. The data are from a single assay but are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Reactivation of l-serine dehydratase with Fe2+ and DTT. Active l-serine dehydratase in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, was exposed to air for 24 h at 4°C until no activity could be detected. The enzyme was then transferred to an anaerobic chamber and was incubated for 1 h at 4°C with FeSO4 at the specified concentrations and with 10 mM DTT in each case. The resulting l-serine dehydratase activities were measured under anaerobic conditions. Reactivation is expressed as a percentage of the activity of the enzyme stored under anaerobic conditions for the duration of the inactivation in air and subsequent reactivation with Fe2+ and DTT.