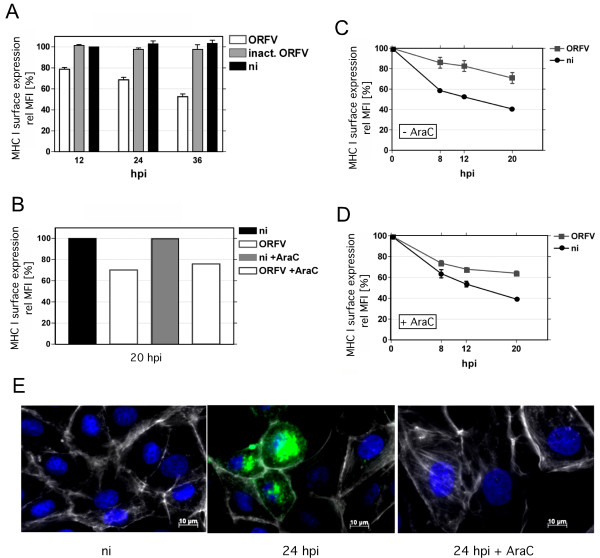
Figure 1.
Modulation of MHC I surface expression in ORFV-infected cells. (A) Vero cells were harvested at 12, 24, and 36 hpi (m.o.i. 1.0) and stained with the anti-MHC I mAb W6/32 as described in Methods. The effect of non-replicating ORFV was tested by the use of ß-propiolactone inactivated ORFV (inact. ORFV; m.o.i. 1.0 before inactivation), non-infected (ni) cells were used as negative controls. The average of three separate virus culturing experiments is shown. ORFV infection decreased cell surface expressed MHC I. (B) Twenty hours post infection (m.o.i. 1.0), MHC I cell surface expression (W6/32) was determined by FACS in the presence and absence of AraC. No effect of AraC treatment on MHC I surface expression was observed. One representative experiment is shown. (C) ORFV infected (m.o.i. 1.0) or non-infected Vero cells were treated with BFA or (D) with BFA plus AraC. Virus infection increased the half-life of MHC I on the cell surface, determined at 8, 12 and 20 hpi using W6/32 anti-MHC I antibody by flow cytometry. The average of three independent experiments is shown in C, D. The relative mean fluorescence intensity (rel MFI) is given in percentages. (E) Infection (m.o.i. 1.0) of Vero cells (green staining) and the effect of AraC was controlled (24 hpi) by immunofluorescence studies using the mAb 13 C10 (diluted 1:1000) recognizing the late major envelope protein of ORFV. Nuclei and F-actin are stained blue by DAPI and white by phalloidin-TRITC, respectively.