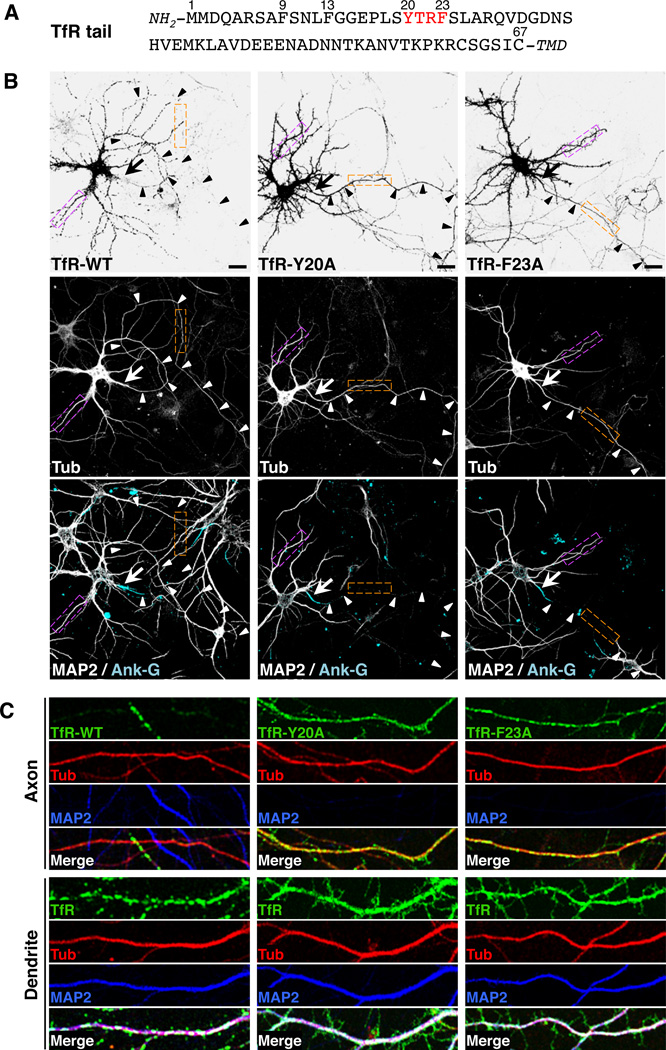
Figure 1. A tyrosine-based motif in the cytosolic tail of TfR is required for its somatodendritic sorting.
(A) Amino-acid sequence of the TfR tail indicating residue numbers and a tyrosine-based YXXØ motif (red). TMD: transmembrane domain.
(B) Neurons (DIV10) expressing monomeric-GFP-tagged TfR-WT, TfR-Y20A or TfRF23A (grayscale negative, top panels) and mCherry-tagged tubulin (Tub, grayscale, middle panels) were double-immunostained for MAP2 (grayscale, bottom panels) and ankyrin G (Ank-G, cyan, bottom panels). In this figure as well as other figures, MAP2 was used as a marker for dendrites and Ank-G as a marker for the axon initial segment (AIS). mCherry-tagged tubulin was a marker for both dendrites and axons. Arrows point to the AIS and arrowheads indicate the axon in each neuron. Scale bars: 20 µm.
(C) Images of axons (top panels) and dendrites (bottom panels) magnified 5X from orange and magenta boxes, respectively, in B. TfR-GFP (green), mCherry-tubulin (red), MAP2 (blue), and merged images are shown. White and yellow in the merged images indicate co-localization. Experiments testing the effects of several amino acid substitutions in the TfR cytosolic tail on the polarized distribution of TfR-YFP and interactions of the TfR cytosolic tail with the µ1A subunit of AP-1 and with the AP-1 core are shown in Figure S1. Surface staining and internalization of YFP-tagged TfR-WT and TfR-Y20A are shown in Figure S2. The effects of amino acid substitutions in the cytosolic tail of CAR on the polarized distribution of GFP-tagged CAR in neurons and on its interaction with the µ1A subunit of AP-1 are shown in Figure S3.