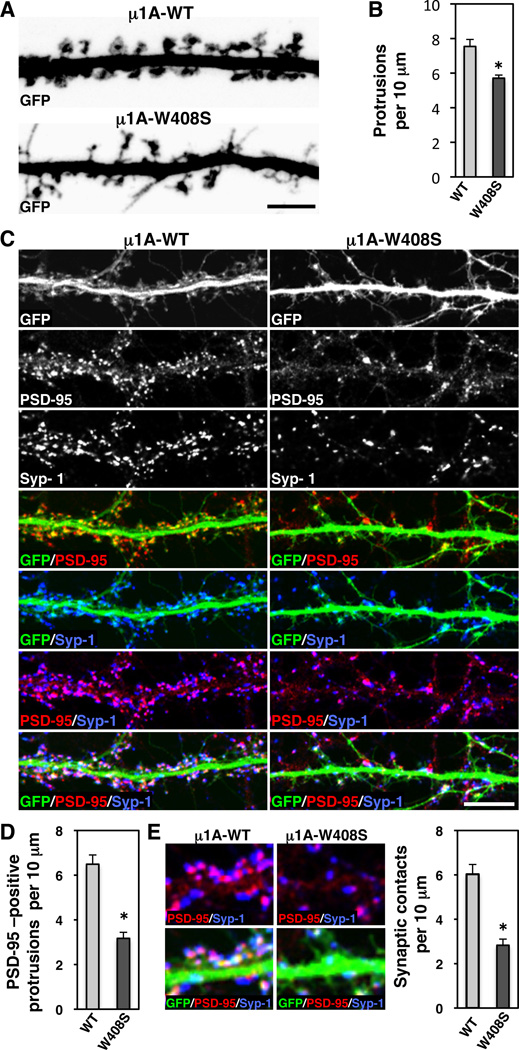
Figure 8. Impaired spine maturation and decreased number of synapses caused by disruption of signal-recognition by µ1A.
(A) Z-stack reconstruction of GFP-positive dendrites (grayscale negative) of neurons (DIV18) co-expressing GFP with HA-tagged µ1A-WT or µ1A-W408S.
(B) Quantification of the protrusion density per 10 µm of GFP-positive dendrite length.
(C) Dendrites from neurons (DIV18) co-expressing transgenic GFP (grayscale and green in merges) with HA-tagged µ1A-WT or µ1A-W408S were stained the excitatory postsynaptic PSD-95 (grayscale and red in merges) and the presynaptic synapsin-1 (Syp-1) (grayscale and blue in merges) markers. Scale bars: 5 µm.
(D, E) Quantification of the protrusions immunoreactive for PSD-95 and synaptic contacts per 10 µm of GFP-positive dendrite length. Images in E (left) show higher magnification of synaptic contacts, observed as apposition of PSD95 (red) and synapsin-1 (blue) in GFP-positive dendrite. In all bar graphs (*) p<0.01.