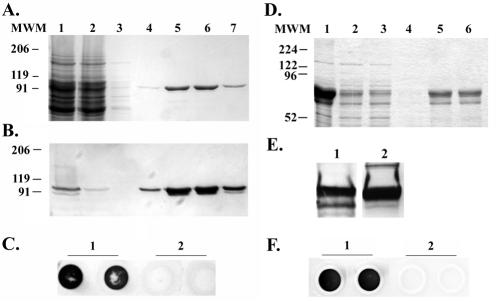
FIG. 1.
Expression and purification of rTbps. (A) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel containing rTbpA protein. Lane 1 contains the soluble fraction after detergent solubilization of induced E. coli. Lanes 2 through 7 represent rTbpA purification fractions. Lane 2 contains the column flowthrough fraction after overnight incubation with a human transferrin-bound affinity column. Lane 3 contains the wash fraction. Lanes 4 through 7 contain purified rTbpA column elution fractions. Molecular weight standards (MWM) are indicated at the left. (B) Western blot of the above SDS-PAGE probed with an anti-TbpA antibody. The positions of molecular weight standards are indicated on the left. (C) Solid-phase transferrin binding assay of purified rTbpA probed with HRP-transferrin (1 μg/ml). Lane 1 contains duplicate spots of purified rTbpA. Lane 2 contains duplicate spots of buffer only. (D) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE containing rTbpB protein. Lane 1 contains a whole-cell lysate of IPTG-induced E. coli. Lane 2 contains the soluble fraction of IPTG-induced, detergent-solubilized E. coli. Lanes 3 through 6 represent rTbpB purification fractions. Lane 3 contains the flowthrough after overnight incubation with a nickel-affinity resin. Lane 4 contains the wash fraction. Lanes 5 through 6 contain purified rTbpB fractions. Molecular weight standards (MWM) are indicated at the left. (E) Western blots of purified rTbpB. Panel 1 was probed with an anti-TbpB antibody. Panel 2 was probed with HRP-transferrin (1 μg/ml). (F) Solid-phase transferrin binding assay of purified rTbpB probed with HRP-transferrin (1 μg/ml). Lane 1 contains duplicate spots of rTbpB. Lane 2 contains duplicate spots of buffer only.