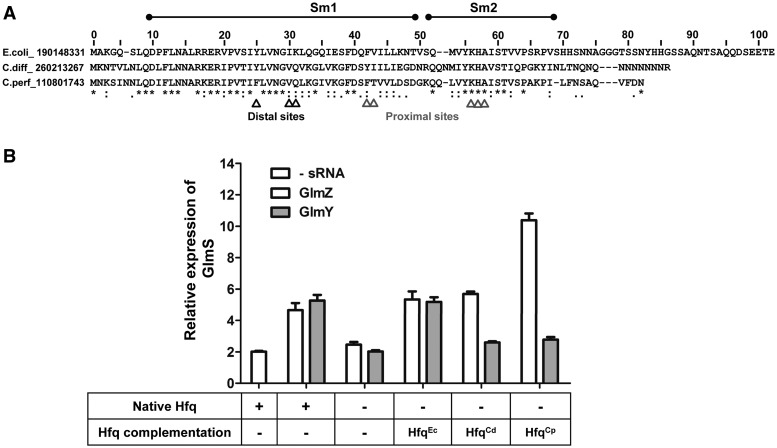
Figure 8.
GlmS:GFP upregulation using C. perfringens and C. difficile Hfq variants by GlmZ and GlmY. (A) Sequence homology between E. coli, C. difficile and C. perfringens Hfq variants. Nucleic acid-binding Sm1/Sm2 domains and important amino acid residues in proximal and distal RNA-binding surfaces required for regulation are indicated. (B) Cross-complementation for HfqEc using HfqCp and HfqCd homologues for GlmS upregulation. The ability to activate GlmS expression by GlmZ and GlmY was measured when HfqCd and HfqCp was supplemented in E.coli Δhfq cells.