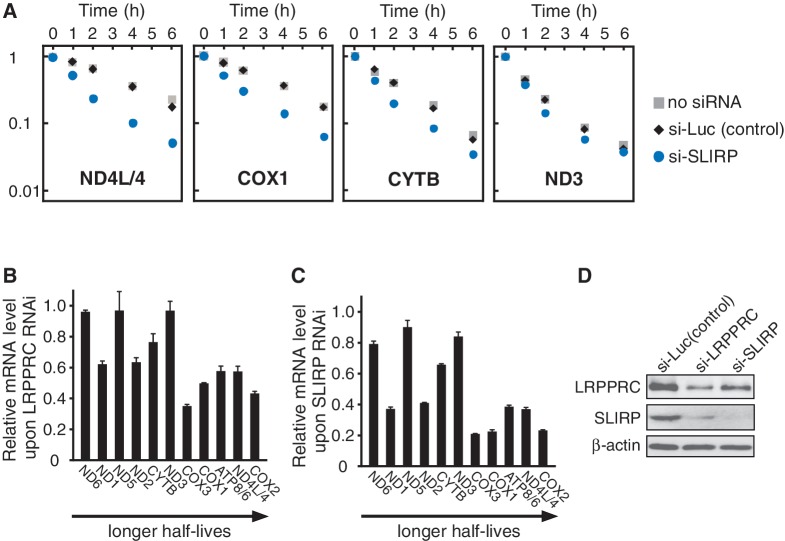
Figure 2.
mRNAs with longer half-lives are stabilized by the LRPPRC/SLIRP complex. (A) Decay of ND4L/4, COX1, CYTB and ND3 mRNAs in HeLa cells after siRNA-mediated knockdown of SLIRP (circles) or luciferase (diamonds) or without siRNA (squares). At 0, 1, 2, 4 or 6 h after the inhibition of mitochondrial transcription, total RNA was collected and each mRNA was quantified by qRT-PCR. All data were normalized to GAPDH mRNA. The vertical axis represents the relative mRNA level in logarithmic scale. The steady-state level of SLIRP mRNA decreased to 3% of that in the control cells upon siRNA-mediated knockdown. (B and C) Relative change in each mRNA level upon LRPPRC knockdown (B) or SLIRP knockdown (C) versus luciferase knockdown control cells, aligned in order of the mRNA’s half-life (5). Mean values with SD were obtained from three independent experiments. The steady-state level of LRPPRC (B) and SLIRP (C) mRNAs dropped to 41% (B) and 1.2% (C), respectively, of those in the control cells. (D) Steady-state levels of endogenous LRPPRC and SLIRP after siRNA-mediated knockdown. Four days after siRNA transfection, endogenous LRPPRC and SLIRP in whole cell lysates were detected by western blotting.