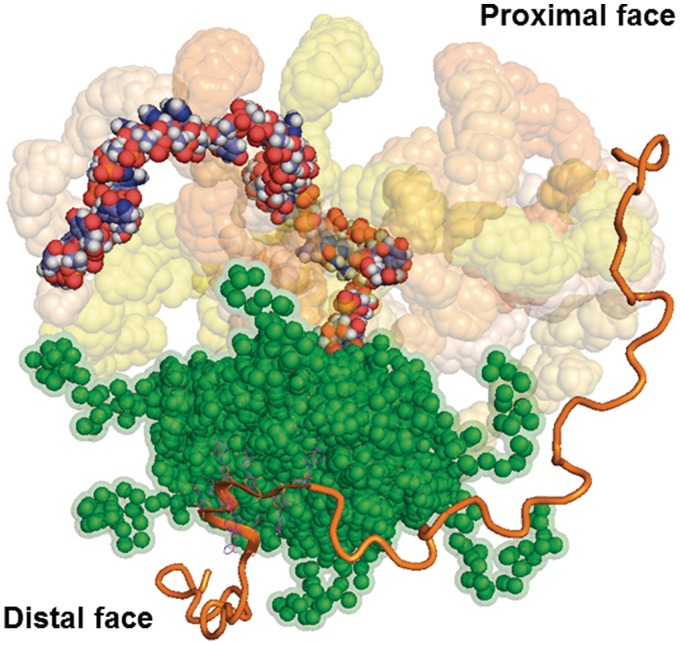
Figure 6.
Model of Hfq RNA chaperone function. The sRNA displayed by the full-atom model with atoms colour-coded is shown bound to the proximal face of HfqEc (green, solvent accessible surface). Through conformational fluctuations, the sRNA can cover a larger conformational space (nine representative DsrA34 models are displayed with their solvent accessible surface coloured as in Figure 5). The mRNA is bound on the distal side (polyA9 orange flat cartoon representation) to one of the six tripartite binding motifs as shown in the crystal structure pdb3GIB (11). The model of a hypothetical mRNA chain is displayed in orange oval cartoon. HfqEc acts by restructuring the mRNA (6), which may be accomplished by the conformationally flexible C-termini (29). The structural variability of both RNAs in a transient ternary 1:1:1 complex (18) would allow to sample large spaces. In this way, HfqEc would not only act as a platform for binding and by increasing the local concentration of both ligands but would also serve to promote their flexibility and consequently successful annealing in a stochastic manner.