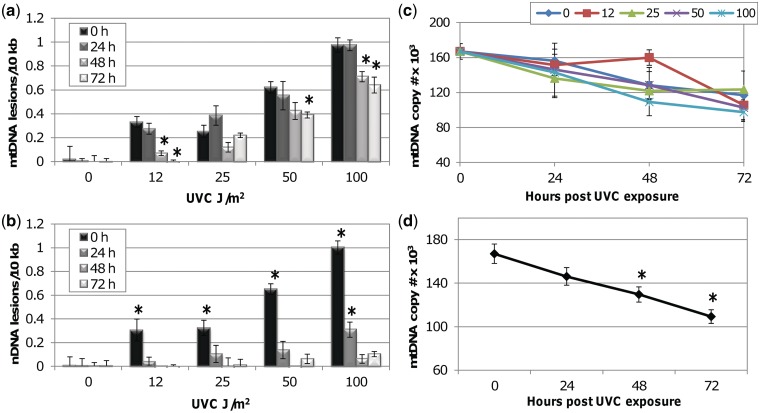
Figure 1.
mtDNA lesion frequency slowly decreases after a single dose of UVC in post-mitotic adult C. elegans (glp-1). Nematodes were exposed to UVC and analyzed for DNA damage immediately (0 h), or after 24, 48 or 72 h via QPCR. (a) mtDNA damage is removed by ∼40% over 72 h at 50 and 100 J/m2. Two-way ANOVA indicated a significant effect of recovery (P < 0.0001) and a recovery × treatment interaction (P < 0.05). Asterisks denote a significant difference compared with 0 h lesion frequency within each UVC treatment (Fisher’s PLSD, P < 0.05). (b) nDNA damage is repaired following a single dose of UVC. Two-way ANOVA indicated a significant effect of treatment (P < 0.0001) and a recovery × treatment interaction (P < 0.0001). Asterisks denote a significant difference compared with undosed control lesion frequency at each recovery timepoint (Fisher’s PLSD, P < 0.05). (c) No significant increase in mtDNA copy number was observed during the recovery period. (d) mtDNA copy number significantly decreased during the recovery period irrespective of UVC exposure. Two-way ANOVA indicated a significant effect of time (P < 0.0001) but no significant treatment effect (P = 0.4714) or treatment × time interaction (P = 0.3246). Asterisks denote a significant difference compared with 0 h mtDNA copy number (Fisher’s PLSD, P < 0.05). Bars ± SEM.