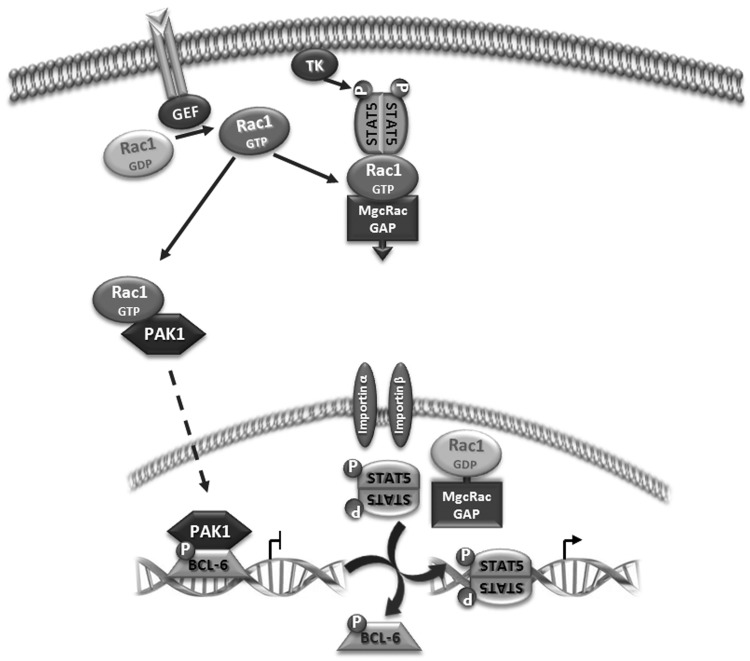
Figure 7.
Proposed model for the role of Rac1 signalling in the observed transcriptional switch. On receptor activation, exchange factors (GEF) promote GTP binding of Rac1 that stimulates two independent pathways. Active Rac1 binds and activates protein kinase PAK1 that migrates into the nucleus and phosphorylates chromatin-bound BCL-6, leading to its inactivation and loss of promoter occupancy. In parallel, a protein complex is formed between active Rac1, MgcRacGAP and STAT5, promoting phosphorylation by a tyrosine kinase (TK) and translocation into the nucleus. Here, MgcRacGAP stimulates GTP hydrolysis by Rac1 and phospho-STAT5 is released and activates gene transcription following binding to the vacant promoter sites previously repressed by BCL-6.