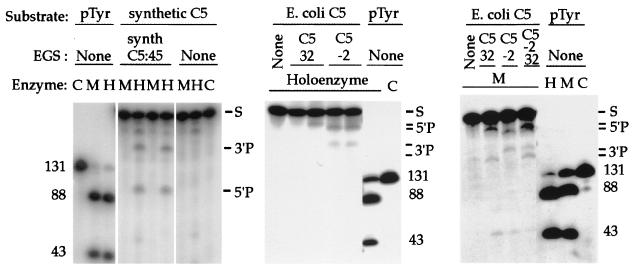
Figure 3.
EGS-directed cleavage of RNA substrate targets in vitro. The components of each reaction mixture are listed above each lane. Target substrates for cleavage include: two preparations of mRNA encoding the C5 protein, one naturally occurring E. coli C5 mRNA (E. coli C5), and one synthetic E. coli C5 mRNA reengineered via conservative codon substitutions (Fig. 1; synthetic C5); as well as precursor tRNA (pTyr). EGSs include an oligonucleotide with sequences complementary to synthetic C5 mRNA, predicted to guide mRNA cleavage at nucleotide 45 (synth C5 EGS:45), and oligonucleotides complementary to naturally occurring E. coli C5 mRNA, predicted to guide mRNA cleavage at nucleotides −2 (C5 EGS:−2) or 32 (C5 EGS:32). Total reaction volumes: 10 μl. RNase P holoenzyme (20 nM M1 RNA and 200 nM C5 protein) was incubated in binding buffer (20 mM Hepes⋅KOH, pH 8/400 mM NH4OAc/10 mM Mg(OAc)2/5% glycerol). M1 RNA (200 nM) was incubated in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5/100 mM NH4Cl/100 mM MgCl2/4% polyethylene glycol. The enzymes were incubated for 15 min in the presence of mRNA substrate (10 nM) and EGS RNAs (50 nM). When the same EGS is listed for more than one otherwise identical enzyme lane, the molar concentration ratio of EGS to target increases from 10× to 50× going rightward. Reference cleavage of precursor to tRNATyr (pTyr) provides size markers, and the target mRNA substrates (S) and cleavage reaction 3′ and 5′ products are indicated. C, no addition other than substrate (control); H, holoenzyme added; M, M1 RNA added.