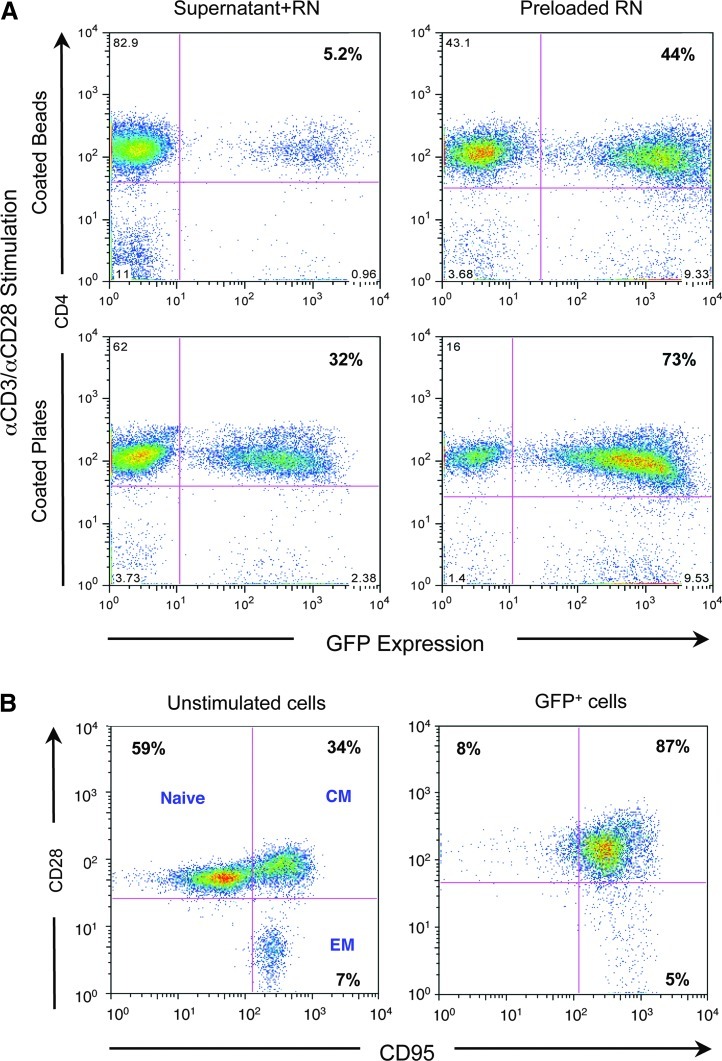
FIG. 2.
In vitro optimization for transduction of macaque CD4+ T cells. (A) Rhesus macaque peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were stimulated for 3 days with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies either immobilized to beads (top row) or to the plate (bottom row) and transduced overnight using an estimated multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 2 transduction units (TU)/cell either directly with supernatants from GaLV-pseudotyped GFP-or intrabody-expressing retroviral vectors (left column) or with supernatants preloaded on Retronectin-coated plates (right column) by spinning at 900×g for 30 min. CD4+ T cells were analyzed for GFP expression after 3 days by flow cytometry. (B) Fresh (left panel) or stimulated (right panel) CD4+ T cells were transduced to express GFP and assessed for expression of CD28 and CD95, molecules which permit categorization of T cells into naïve, central memory (CM), and effector memory (EM) populations.