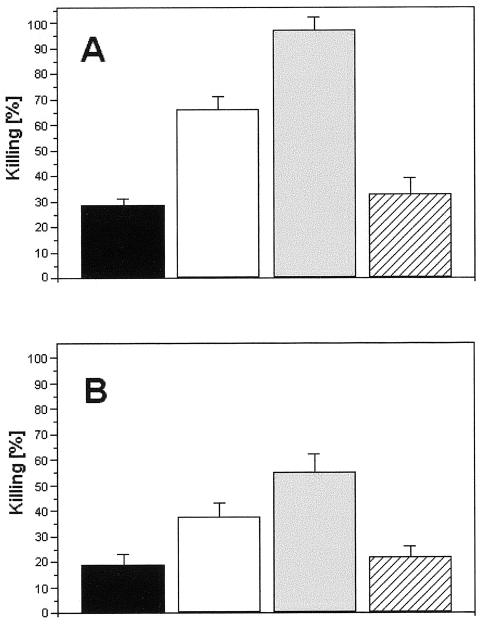
FIG. 8.
Killing of F. pedrosoi conidia (A) or sclerotic cells (B) after interaction with human neutrophils. Black bars, percentage of killing of fungal cells after interaction with neutrophils. Supplementation of the medium of interaction with melanin (white bars) or melanin antibodies (gray bars) significantly enhanced the antifungal efficacy of neutrophils, while the association between these components (hatched bars) resulted in levels of fungal death similar to those observed in the absence of antibodies or soluble melanin. Values of P and statistical significance are described in Results. Data are expressed as means of three independent experiments ± standard deviations.