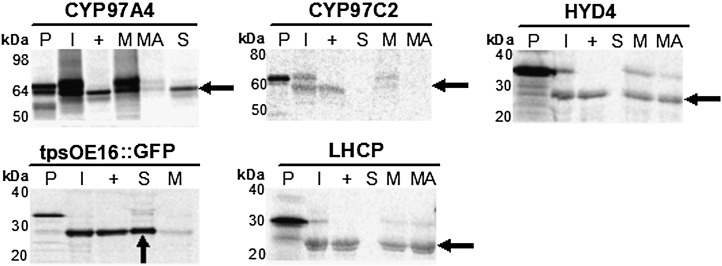
Figure 4.
Chloroplast import assays of CYP97 and diiron HYD proteins. Isolated pea chloroplasts were used for in vitro import of [35S]Met-radiolabeled protein precursors. Chloroplasts harboring imported proteins were then reisolated and subjected to thermolysin treatment to distinguish between proteins that were peripherally bound to the outer chloroplast envelope and those that had been imported and thus processed to remove the transit peptide. The mature proteins were recovered as protease-resistant forms (arrows), confirming the import of these proteins into chloroplasts. Chloroplasts containing imported proteins were hypotonically lysed and fractionated into soluble and membrane fractions. The pellet fractions were then treated with an alkaline buffer to wash away peripherally associated membrane proteins. The purity of fractions was controlled by import and fractionation analysis of a chloroplast lumen protein, tpsOE16::GFP (Marques et al., 2003), and the integral thylakoid membrane-bound protein, LHCP (Tan et al., 2001). SDS-PAGE analysis of chloroplasts and their fractions indicated that CYP97A4 and CYP97C2 were synthesized as precursors of about 69 and 62 kD and then processed to 64 and 59 kD, respectively. HYD4 was synthesized as a precursor of roughly 34 kD and processed to 27 kD. P, Translation products; I, imported protein; +, thermolysin treatment; S, soluble proteins; M, membrane proteins; MA, alkaline-treated membrane fraction.