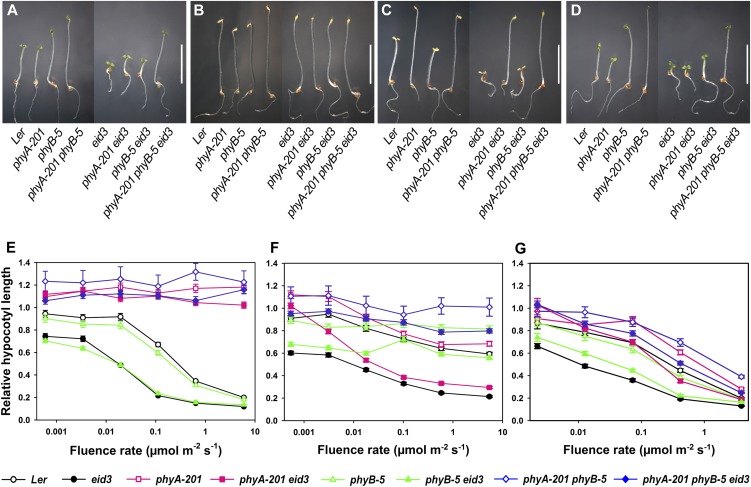
Figure 1.
Epistatic analyses with phyA and phyB loss-of-function mutants. A to D, Photographs of Ler wild-type, phyA-201, phyB-5, phyA-201 phyB-5, eid3, phyA-201 eid3, phyB-5 eid3, and phyA-201 phyB-5 eid3 seedlings grown under different light conditions for 4 d after induction of germination. Seedlings were kept under the screening program (cycles of 20 min of red light followed by 20 min of far-red light; A), in darkness (B), under weak far-red light (0.1 µmol m−2 s−1; C), and under weak red light (1 µmol m−2 s−1; D). Bars = 5 mm. E to G, Fluence rate response curves for the inhibition of hypocotyl elongation of Ler wild-type, phyA-201, phyB-5, phyA-201 phyB-5, eid3, phyA-201 eid3, phyB-5 eid3, and phyA-201 phyB-5 eid3 seedlings under continuous far-red light (E), continuous red light (F), or continuous blue light (G). Relative hypocotyl lengths were calculated in relation to the length of dark-grown seedlings for each line. Each data point represents the mean ± se of two independent experiments with at least 30 seedlings.