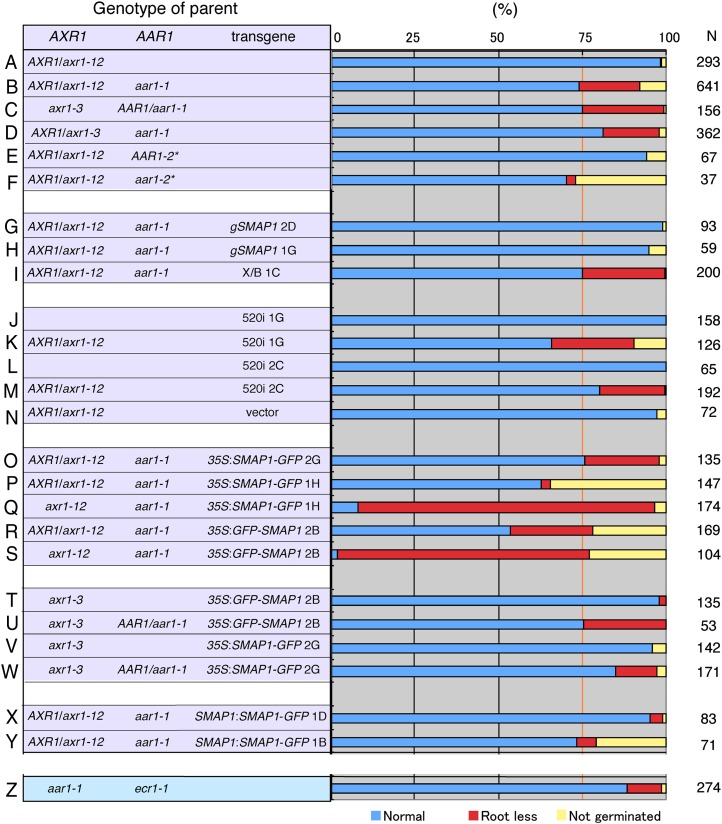
Figure 2.
Frequency of rootless seedlings in various genetic backgrounds. Frequency of normal (blue), rootless (red), and nongerminated (yellow) phenotypes in offspring seedling populations from parent plants of the indicated genotypes is shown. N indicates the number of seedlings observed. The vertical orange line highlights the 3:1 expected ratio for normal:abnormal seedlings from parent lines. Because the axr1 aar1 double mutant was postembryonic lethal, seeds harvested from the AXR1/axr1 heterozygote background were tested in most of the experiments. Transgenes were introduced by crossing. A to F, Phenotype of axr1 aar1 double mutants. * Wassilewskija accession. G to I, Complementation of the rootless phenotype of axr1 aar1 by a genomic fragment containing SMAP1 (gSMAP1). A genomic fragment (X/B) without SMAP1 was used as a control (I). Two independent transgenic lines for gSMAP1 (B/S lines 2D and 1G) and the control line X/B line 1C with the aar1-1 mutation (Rahman et al., 2006) were crossed with axr1-12 mutants to generate parental lines. J to N, Inactivation of SMAP1 by RNAi in the axr1 background. Two independent 520i lines (lines 1G and 2C) or a control line (line F2) transformed with vector pB7GWIWG2(II) (Rahman et al., 2006) were crossed with axr1-12 mutants to generate parental lines. O to W, Expression of the SMAP1∼GFP fusion protein under the control of the 35S promoter in the axr1 aar1 background. Transgenic lines of 35S:SMAP1-GFP/aar1-1 (lines 2G and 1H) or 35S:SMAP1-GFP/aar1-1 line 2B (Supplemental Fig. S1) were crossed with axr1-12 (O–S) or axr1-3 (T–W) mutants. X and Y, Complementation of the rootless phenotype of the double mutant by SMAP1:SMAP1-GFP. Two independent transgenic lines (D4 and B4) of SMAP1:SMAP1-GFP/aar1-1 were crossed with the axr1-12 mutant to generate parental lines. Z, The rootless phenotype was observed in approximately 10% of aar1-1 ecr1-1 seedlings.