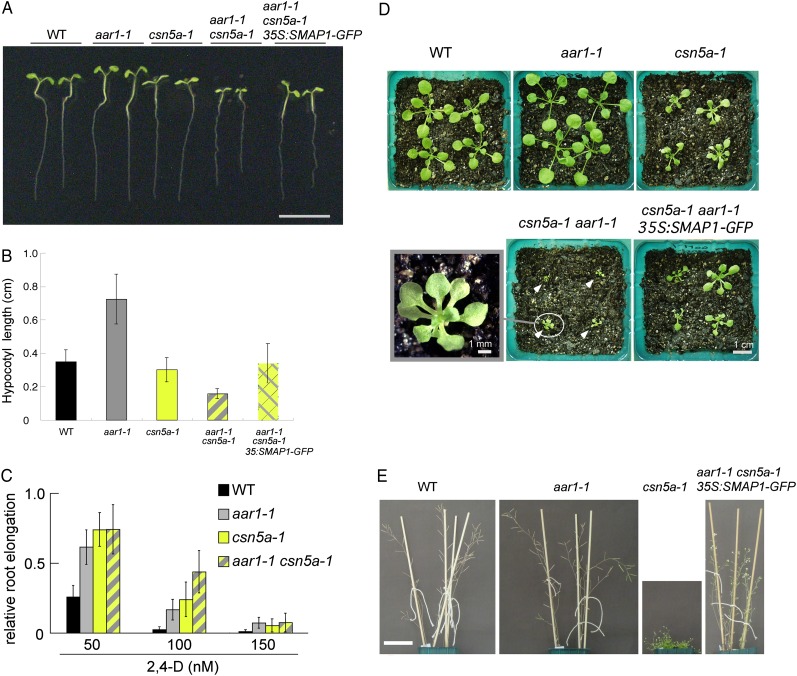
Figure 6.
Genetic interaction of CSN5A and SMAP1. We could not obtain a sufficient number of seeds of the aar1-1 csn5a-1 double mutant; therefore, dwarf aar1-1 csn5a-1 seedlings were selected from a seed population from the aar1-1 CSN5A/csn5a-1 parental line for analysis. A and B, Images (A) and root lengths (B) of 7-d-old seedlings grown on GM without growth regulators. Bar in A = 1 cm. Values in B are means ± sd (n = at least 13 seedlings). C, Seeds were germinated and grown on GM for 4 d and then transferred onto GM containing 2,4-D at the indicated concentrations and grown for an additional 3 d. Root elongation after transfer was measured and plotted as a relative value compared with that on medium without chemicals. Values are means ± sd (n = at least 17 seedlings). Mean values (cm) ± sd in the absence of chemicals controlling root elongation were as follows: 1.56 ± 0.18 (wild type [WT]), 1.64 ± 0.22 (aar1-1), 1.71 ± 0.30 (can5a-1), and 1.21 ± 0.22 (aar1-1 csn5a-1). D, Photographs of plants at the rosette stage. Seeds were germinated on GM and grown for 9 d, and seedlings were then transferred to soil and grown for an additional 11 d under 16-h-light/8-h-dark conditions. White arrowheads indicate aar1-1 csn5a-1 double mutants. The photograph at bottom left is an enlarged image of a aar1-1 csn5a-1 double mutant. E, Photographs of adult plants. Seeds were germinated and grown on GM for 9 d, and seedlings were then transferred to soil and further grown for 35 d under 16-h-light/8-h-dark conditions. Bar = 5 cm.