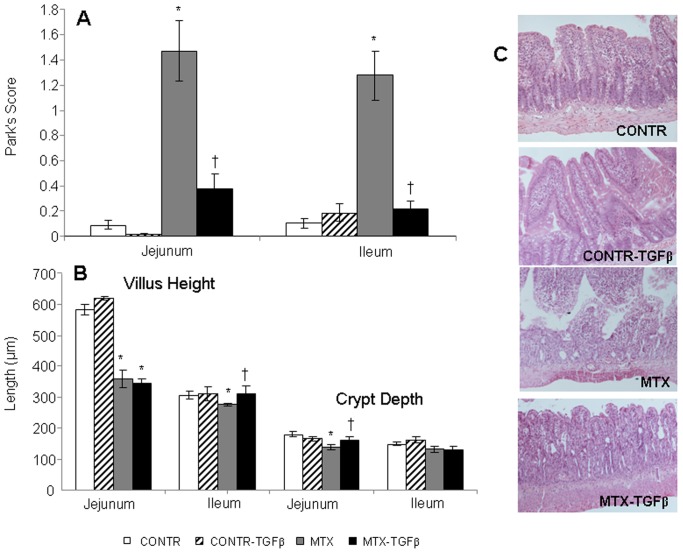
Figure 6. Effect of TGF-β on intestinal injury score and microscopic intestinal appearance following MTX-induced mucositis.
The degree of intestinal tissue injury was evaluated on a grading scale from 0 to 8 as described previously by Park (A). The villus height and crypt depth were measured using the Image Pro plus 4 image analysis software (B). (C) Representative slides of MTX-induced intestinal injury. The histopathology analysis of the tissue sections from MTX-treated animals showed a significant epithelial atrophy, blunting of the villi and signs of crypt remodeling that was accompanied by marked cellularity mainly by mononuclear cells in the lamina propria, the presence of the flattened and vacuolated cells, and an increased number of blood vessels in the stroma. TGF-β2 administration resulted in less significant epithelial atrophy and crypt remodeling compared to MTX rats. Values are mean ± SEM. CONTR-control, MTX-methotrexate, TGF-β- transforming growth factor beta. *P<0.05 MTX and MTX-TGF-β versus control, †P<0.05 MTX-TGF-β versus MTX rats. CONTR-control,