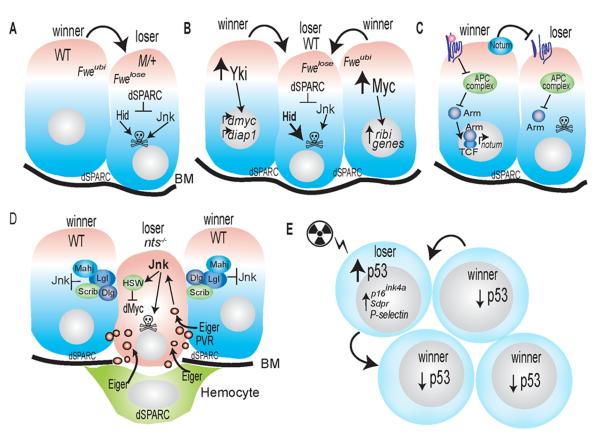
Figure 1. Modes and mechanisms of cell competition.
A. Cell competition between Minute/+ and wildtype cells. Wildtype cells (winners) outcompete M/+ cells (losers). Confrontation leads to alternative splicing of Fwe in the loser cells, and expression of the Fwelose isoform. dSparc is expressed temporarily in loser cells, transiently protecting the cells from apoptosis. Sparc is also expressed constitutively in the basement membrane (BM) of discs and in hemocytes. Neither loss of NST genes and basal membrane disruption is required to trigger M/+ induced cell competition. JNK is activated and contributes to death of loser cells, but inhibition of JNK signaling is not sufficient to prevent their elimination.
B, C. Super-competitors versus wildtype cells. Activation of dMyc, Yki (B) or Wg/Wnt (C) signaling leads to super-competitive behavior. The Fwelose isoform and dSparc are expressed in loser cells in response to dMyc super-competition. Activation of Yki confers super-competitive properties to cells largely due to dMyc upregulation.
C. Binding of Wg to its receptors inhibits the APC complex, resulting in nuclear translocation of Armadillo/β-Catenin (Arm) and target gene expression. Loss of components of the APC complex hyper-activates Wg signaling. Competition induced by Wg occurs independently of dMyc, but requires production of Notum (Nt), a secreted hydrolase that modifies heparan sulfate proteoglycans.
D. Neoplastic Tumor Suppressors. Lethal Giant Larvae (Lgl), Scribble (Scrib) and Disc-large (Dlg) are NTSs and exist in a complex. Mahjong (Mahj) is a binding partner of Lgl. Nts mutant cells are at a disadvantage in mosaic tissues. Reduction of dMyc expression occurs in lgl mutant cells and contributes to their death. Elimination of nts mutant cells also occurs through Eiger-mediated activation of JNK signaling and apoptosis. Loss of apical-basal polarity damages the basement membrane (BM) and attracts hemocytes. A non-autonomous source of Eiger/TNF is required to activate JNK; the relative contribution of surrounding wildtype disc cells versus local hemocytes is unclear. Eiger is taken up via endocytosis in the mutant cells (red bubbles). PVR expression in wildtype cells promotes engulfment of the nts mutant cells.
E. Cell competition in murine HSPCs. In stressed mouse HSPCs, the relative level of p53 determines whether cells are winners or losers. Cells with less or mutant p53 become winners and proliferate more. Cells with activated p53 status are losers, but these cells acquire a senescent state and express markers such as p16, Sdpr, and P-selectin, rather than die by apoptosis. The presence of each competitor cell type is required for the altered gene expression profiles and behaviors (arrows).