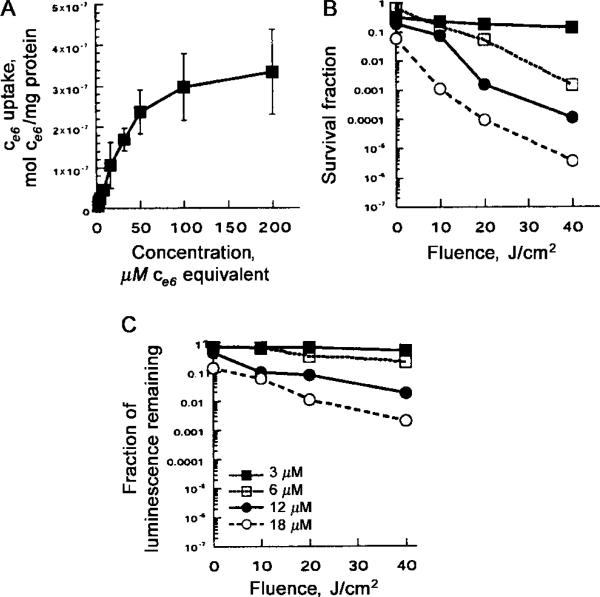
Figure 1.
A, Uptake of ce6 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, after 30 min of incubation in PBS with stated concentrations of poly-L-lysine–ce6, followed by dissolution of cell pellet in NaOH–SDS and fluorescence and protein assays. Data points are means of triplicate determinations and 2 separate experiments, and bars indicate SDs. B and C, Phototoxicity, as determined by either colony-forming unit assay (B) or luminescence assay (C). Bacteria were incubated with conjugate and then were washed and were illuminated by fluences (0, 10, 20, and 40 J/cm2) of 665-nm light, by removing aliquots of bacterial suspension at intervals at 0, 100, 200, and 400 s, respectively, followed by serial dilution and plating or luminescence measurement in 96-well plates. Data points are means of triplicate determinations and 2 separate experiments, and bars indicate SDs.