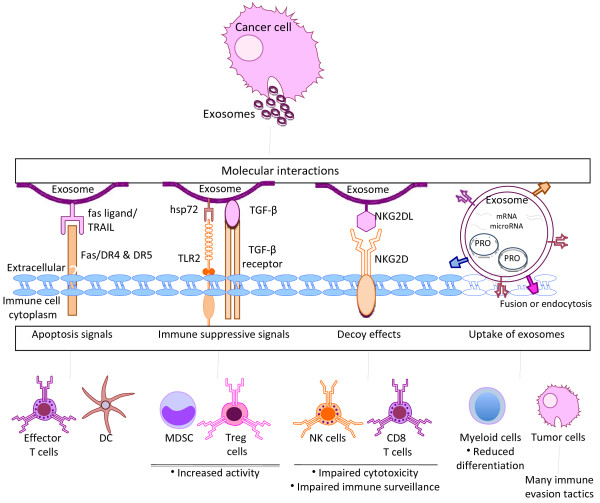
Figure 1 .
Mechanisms of immune tolerance mediated by tumor-derived exosomes. Exosomes evoke numerous immune suppressive pathways during their interactions with immune cells. Depicted are examples of immune suppressive interactions between tumor-derived exosomes and immune cells and their downstream effects on specific immune functions. Examples of direct adhesion and signaling interactions between surface-expressed proteins on immune cells are depicted, whereby exosomes elicit apoptosis signaling, induction of immune suppressive activity, and blockade of receptors/ligands required for anti-cancer immunity. Alternatively, exosomes and/or their contents, including proteins (PRO) and genetic material (mRNA and microRNA), are delivered directly into target cells via exosomal fusion with the target cell membrane or endocytosis. Cells that reportedly take up exosomes include immune cells (example shown) and tumor cells, which are endowed with the ability to evade immune responses through the horizontal transfer of exosomal cargo.