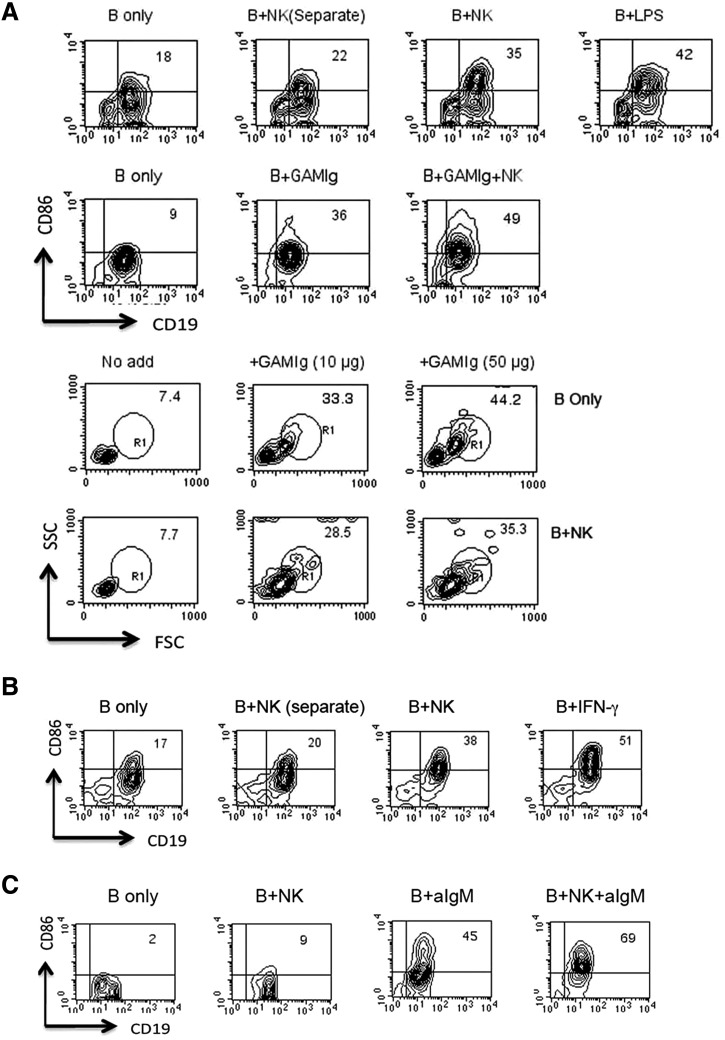
Figure 4. Enhancement of B cell differentiation by IL-2-propagated or freshly isolated NK cells.
CD43-negative, Percoll-fractionated resting B cells were cultured for 18 h in the presence of additives, as indicated alone or together with splenic NK cells isolated from IFN-γ0/0 mice, which were propagated for 7 days in IL-2 (A) or not propagated (B). B + NK (Separate) indicates B and NK cells cultured separately but combined before analysis to ensure appropriate gating. B cell activation was assessed by increases in CD86 (BioLegend) expression on CD19-positive cells and by blast transformation indicated by increases in forward (FSC)- and side-scatter (SSC) of NKp46-negative cells. Results shown in A and B are representative of two or three independent experiments. (C) B cells isolated from IFNAR0/0 mice were cultured with freshly isolated NK cells in the presence or absence of goat anti-IgM (GAMIg; aIgM) for 20 h before analysis by FACS (results are representative of two independent experiments).