Figure 4.
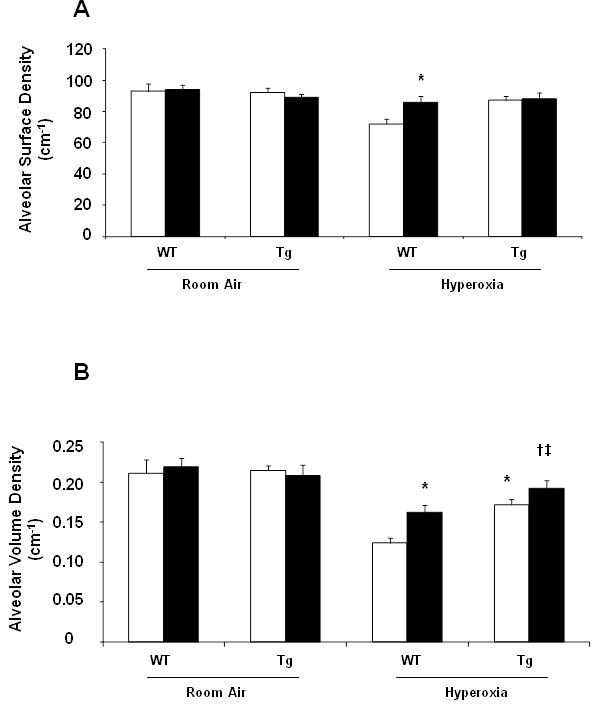
Alveolar surface density (A) and volume density (B) of WT and Tg mice ± Antileukinate (■ treated, □ non-treated) after 7 day-exposure to air or 95% O2. Following exposure to 95% O2, in WT mice, Antileukinate significantly improved both alveolar surface and volume density. In Tg mice, Antileukinate also significantly improved alveolar volume density. However, there was no difference in alveolar surface density. Tg mice also significantly improved alveolar volume density compared to WT counterpart groups after hyperoxic exposure. Data are mean of five animals per group ± SEM. * p < 0.05 when compared to Antileukinate-non-treated WT/H, †p < 0.05 when compared to Antileukinate-treated WT/H, ‡p < 0.05 when compared to Antileukinate-non-treated Tg/H. (RA: room air, H: hyperoxia).
