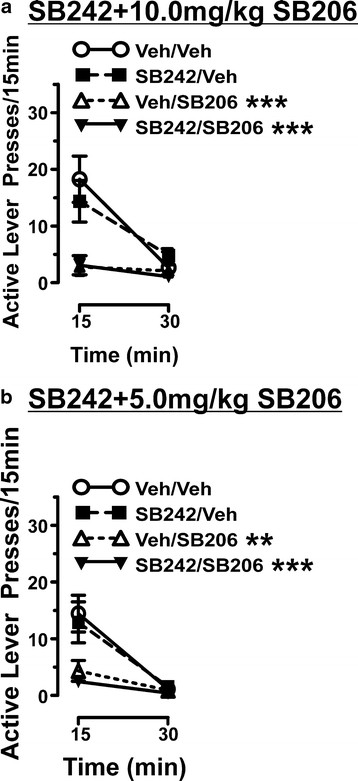
Figure 4.
Attenuation of active lever pressing by SB206 was not reversed by the 5-HT2Cantagonist SB242. Shown are active lever presses in 15 min intervals for the first 30 min of cue reactivity (CR) testing from rats that completed interaction studies with 3.0 mg/kg SB 242084 (SB242) vs. 10.0 mg/kg SB 206553 (SB206; n = 11) or 5.0 mg/kg SB206 (n = 9; one statistical outlier removed). Rats were tested after a pretreatment of vehicle or 3.0 mg/kg SB242, and vehicle, 5.0, or 10.0 mg/kg SB206. The x-axis legend refers to time elapsed after treatment and immediately placing the subject into the operant chamber; data represent total active lever presses between 30-45 min and 45-60 min after treatment. (A) 5-HT2C antagonism with 3.0 mg/kg SB242 had no effect on CR when administered alone and did not block the effects of 10.0 mg/kg SB206. SB206 significantly decreased active lever presses in the first 15 min of testing (***p < 0.001; Newman-Keuls comparing veh/veh vs. 10.0 mg/kg SB206) and significance was retained even following pretreatment with SB242 (***p < 0.001; comparing veh/veh vs. SB242/SB206). (B) 5-HT2C antagonism with 3.0 mg/kg SB242 had no effect on active lever pressing when administered alone and did not block the effects of 5.0 mg/kg SB206. SB206 significantly decreased active lever presses in the first 15 min of testing (**p < 0.01; Newman-Keuls comparing veh/veh vs. 5.0 mg/kg SB206) and significance was retained following pretreatment with SB242 (***p < 0.001 comparing veh/veh vs. SB242/SB206).