Figure 6. Saturation of the receptive field for both local and global stimuli makes short timescale response insensitive to the spatial extent of electrosensory stimuli.
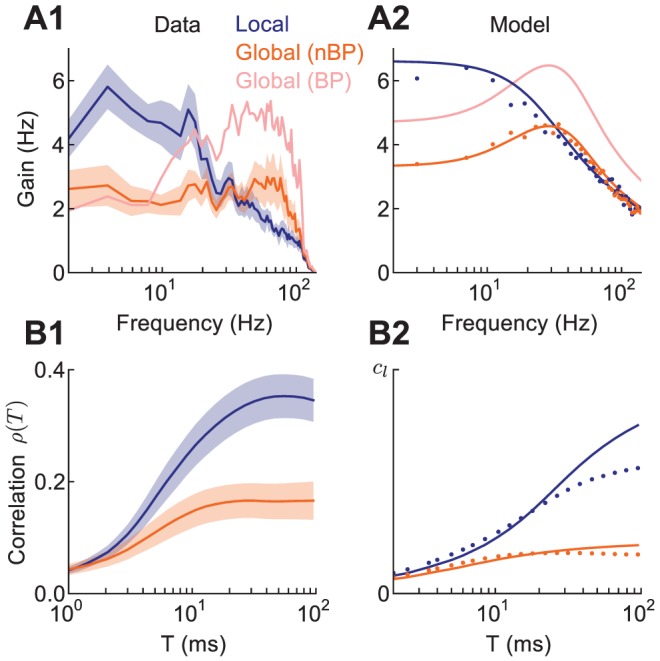
A1, Experimental stimulus gain for nBP neurons (n = 14) in local and global stimulus configurations. The gain for BP neurons in the global configuration is shown for comparison (see Figure 2B). A2, Stimulus gain for model nBP neurons (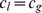 ) in local and global configurations, and the model BP neurons (
) in local and global configurations, and the model BP neurons (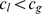 ) in global for comparison. B1, Recorded spike count correlation over windows of length
) in global for comparison. B1, Recorded spike count correlation over windows of length 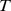 for pairs of nBP neurons. As with BP neuron pairs, firing rates in the local and global states were similar (
for pairs of nBP neurons. As with BP neuron pairs, firing rates in the local and global states were similar (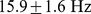 and
and 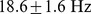 , respectively). B2, Spike count correlation for pairs of model nBP superficial neurons in the ELL-EGp network. For the model results (A2,B2) our analytical theory (solid) matches the simulation results from the ELL-EGp network (dots). Values are shown in units of input correlation in the local state
, respectively). B2, Spike count correlation for pairs of model nBP superficial neurons in the ELL-EGp network. For the model results (A2,B2) our analytical theory (solid) matches the simulation results from the ELL-EGp network (dots). Values are shown in units of input correlation in the local state 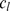 .
.
