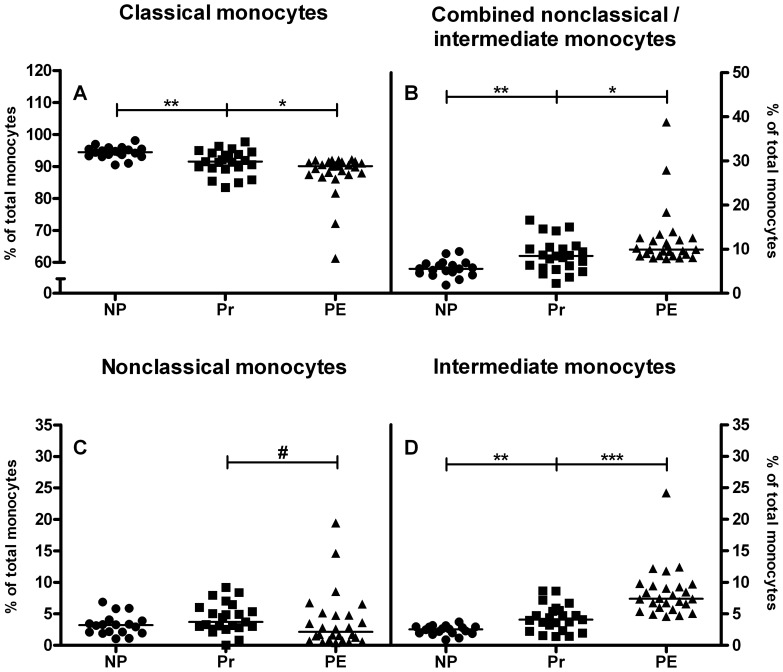
Figure 3. Human monocyte subsets in peripheral blood.
Lower percentages of classical monocytes were observed in healthy pregnant women (Pr, squares) as compared to nonpregnant women (NP, circles) and even less in preeclamptic women (PE, triangles) compared to healthy pregnant women (A). Higher percentages of combined nonclassical/intermediate monocytes were found in pregnant women compared to nonpregnant women and even higher percentages in preeclamptic patients compared to healthy pregnant women (B). When subdividing into nonclassical and intermediate monocytes, no significant changes were observed in nonclassical monocytes (C), though a trend towards lower nonclassical monocytes was observed in preeclamptic women compared to healthy pregnant women. In contrast, higher percentages of intermediate monocytes were found in healthy pregnant women compared to nonpregnant women and even higher percentages in preeclamptic patients compared to healthy pregnant women (D). Medians are shown, #p<0.1, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; Mann Whitney U test.