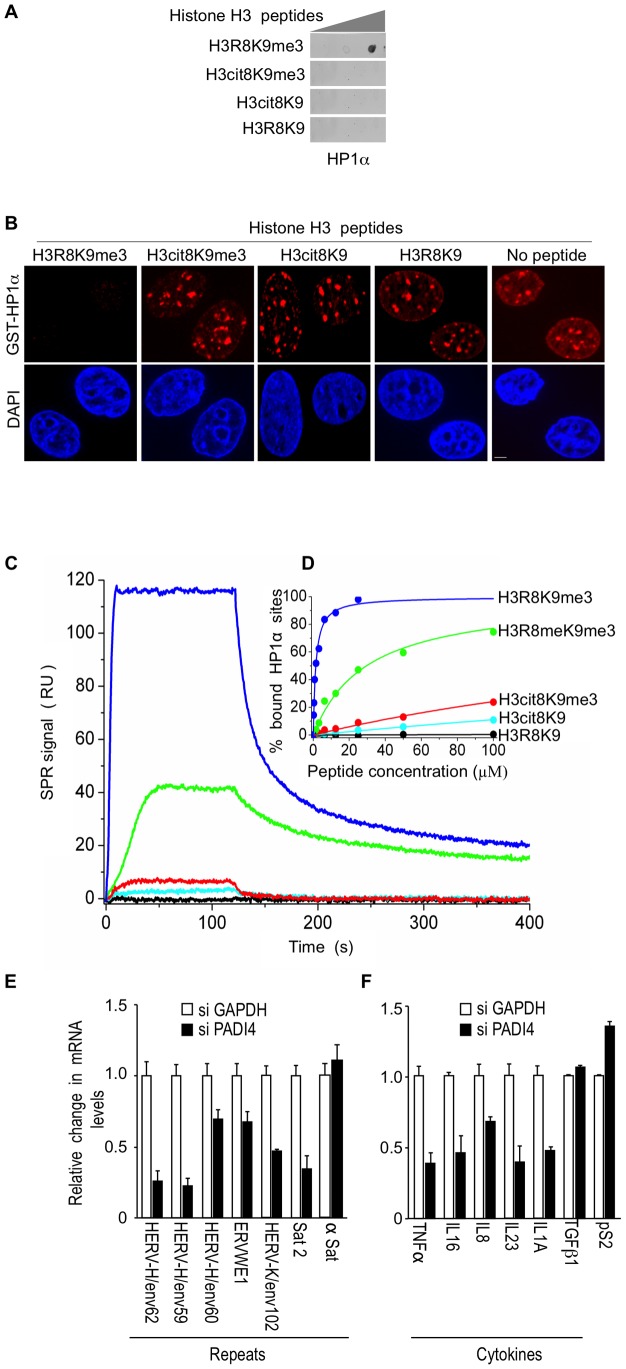
Figure 3. The H3cit8K9me3 double histone modification reduces the affinity of HP1α for the H3K9me3 single modification.
(A) Dot blot showing that HP1α does not bind to histone H3 peptides carrying a H3Cit8K9me3 double modification. Indicated histone H3 peptides of 1, 0.2, and 0.04 µg were spotted on the membranes. Then binding of recombinant GST-HP1α was tested by labeling of the retained protein with anti-GST antibodies. Blots are representative of the experimental replicates. (B) Purified recombinant GST-HP1α (red) was bound to fixed MCF7 cells in “overlay” assays, and then challenged by competition with 1 µg of the indicated peptides. DNA is labeled with DAPI (blue), scale bar: 5 µm. (C) Real-time association and dissociation surface plasmon resonance (SPR) profiles corresponding to the injection of the indicated H3 peptides at 12.5 µM over immobilized GST-HP1α. (D) Percentage of bound GST-HP1α sites as a function of the peptide concentration. (E–F) Total RNA from MCF7 cells transfected with the PADI4 small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) was quantified with RT-qPCR. Changes in mRNA levels are shown relative to the siGAPDH transfection (set to 1), which was not affecting the mRNA levels of the genes of interest (Figure S1C). The data are presented as the means ± SEM of triplicate experiments.